Variables
Generalities
Rudder has a notion of variables. A variable is something with a name that references a value, and that value can be accessed with appropriate syntax around its name. We call accessing the value variable expansion in honor to shell, guarding totem of devops glue.
In Rudder, variable name are namespaced with a dotted convention. Values can be mainly of two types: string and json, i.e. dictionary-like recursive structures. Rudder only supports UTF-8 for variables names and values.
Under that broad notion of variable, we need to take apart the two main action around them:
-
how one defines them?
-
and how one uses them?
In each case, we have sub-cases directed by use.
Variables definition covers two big aspects of knowledge:
-
configuration data, known by humans when policies are defined. That knowledge needs to be centralized, categorized, hierarchized and retrieved based on which node policies will be used,
-
dynamic or contextualized information about infrastructure provided by environment tooling, be it Rudder itself, facts about environment, or resources available only when the policy is checked.
In Rudder, how one reference a variable and when it will be expanded to retrieve its value depends upon where it is used. There is three cases:
-
use in a techniques (in the editor or if you directly write generic methods),
-
use in directives parameters,
-
and use in templates (jinja2 or mustache).
The following sections will cover these notions and how to apply them in Rudder to fulfill your use cases.
An overview of variables is available in Rudder cheatsheet.
Variables definition purpose: configuration data or source of environment knowledge?
In Rudder, we distinguish between two main cases for variable definition:
-
1/ configuration data that depicts business knowledge about their infrastructure. That data is organized around node and groups of nodes, in hierarchies that allow to refine and special cases values from general cases and default values to node. That data is stored on the Rudder server, versioned along configuration logic and is available when policies are generated for each node.
A typical example for configuration data is the DNS server to use. The value is part of IT ops knowledge and will be different if the node is in a datacenter or another.
-
2/ source of environmental information, that are generally provided by Rudder or directly on the node and often represent facts about your infrastructure. That data is not known when policies are generated but only when policies are checked and can change from a check to the next depending of environmental changes, so that that data can’t be versioned along configuration logic.
A typical example of facts is the result of a command (node environment) or the node’s policy server IP (Rudder provided information).
The exact syntax to access a variable’s value, especially in the case of JSON values, depends of where it’s used. By convention, when table of variables are presented below, they will clearly explain what is the variable name. It will also present dictionary keys (which are also names) in a dotted path syntax. Exact syntax for the three use cases will be reminded each time.
Hierarchical configuration data with node properties
Assigning the correct value to a configuration process is as much important as knowing how the process must be done. Configuration data are an extremely important part of our work, and we must ensure that they remain consistent across all configuration. To answer that problem, Rudder provides the notion of node properties that allows to define values of variables for each node and takes advantage of Rudder existing node categorization in groups to inherit commons values.
More precisely, a node property is a name=value pair. The value can be a string or a well-formatted JSON data structure.
Some examples:
-
datacenter=Paris -
datacenter= { "id": "FRA1", "name": "Colo 1, Paris", "location": "Paris, France", "dns_suffix": "paris.example.com" }
A node property can be define at three levels with inheritance between each of them. These level are, starting from the more general to the most specific:
-
global parameters, which are properties defined on all nodes and are useful to define common knowledge and default values,
-
group properties that are defined in groups. Only nodes of that group get corresponding properties. Group properties are inherited from global parameters and properties define in parent groups,
-
node properties, which are properties defined directly on the node.
At each level, properties can be defined via UI or via API. For nodes, external properties, typically from a CMDB, can be synchronized thanks to data source plugin.
Variable expansion is done during policy generation so that variable knows their final value at that moment, and it doesn’t change until the next generation.
A last level of overriding is available directly locally on node. Since that part is not about configuration data known when policies are generated, it will be covered in the next section.
Inheritance and overriding
Properties are inherited from global parameters to groups, then from groups to subgroups, and then from groups to nodes.
At each step, all properties from parent that are not defined in children are added to the latter. For properties with a common name, an override is done with a configurable algorithm, which by default overrides string values and arrays (i.e the child value is kept), and merge object as follow:
-
if child value is a string, it is kept,
-
if parent value is a string and child one is a JSON, JSON is kept
-
if parent value is a JSON array and child is a JSON object, child value is kept,
-
if parent value is a JSON object and child is a JSON array, child value is kept,
-
if both values are JSON array, child array is kept,
-
if both values are JSON object, object are merged using current algorithm recursively: missing keys are added, etc.
You can choose the behavior for each of string, array or object cases independently and at each level (global parameters by UI or API, group properties and node properties by API) with a string of tree letters alike file permissions string:
-
first letter is for object. Possible values are 'm' (merge object, default), or 'o' (override)
-
second letter is for array. Possible values are 'o' (override, default), 'a' (append child value to parent), or 'p' (prepend child value to parent)
-
third letter is for strings. Possible values are 'o' (override, default), 'a' (append child value to parent), or 'p' (prepend child value to parent)
Example of setting the value for a global parameter to 'maa' (override object, append array and strings) in the UI:
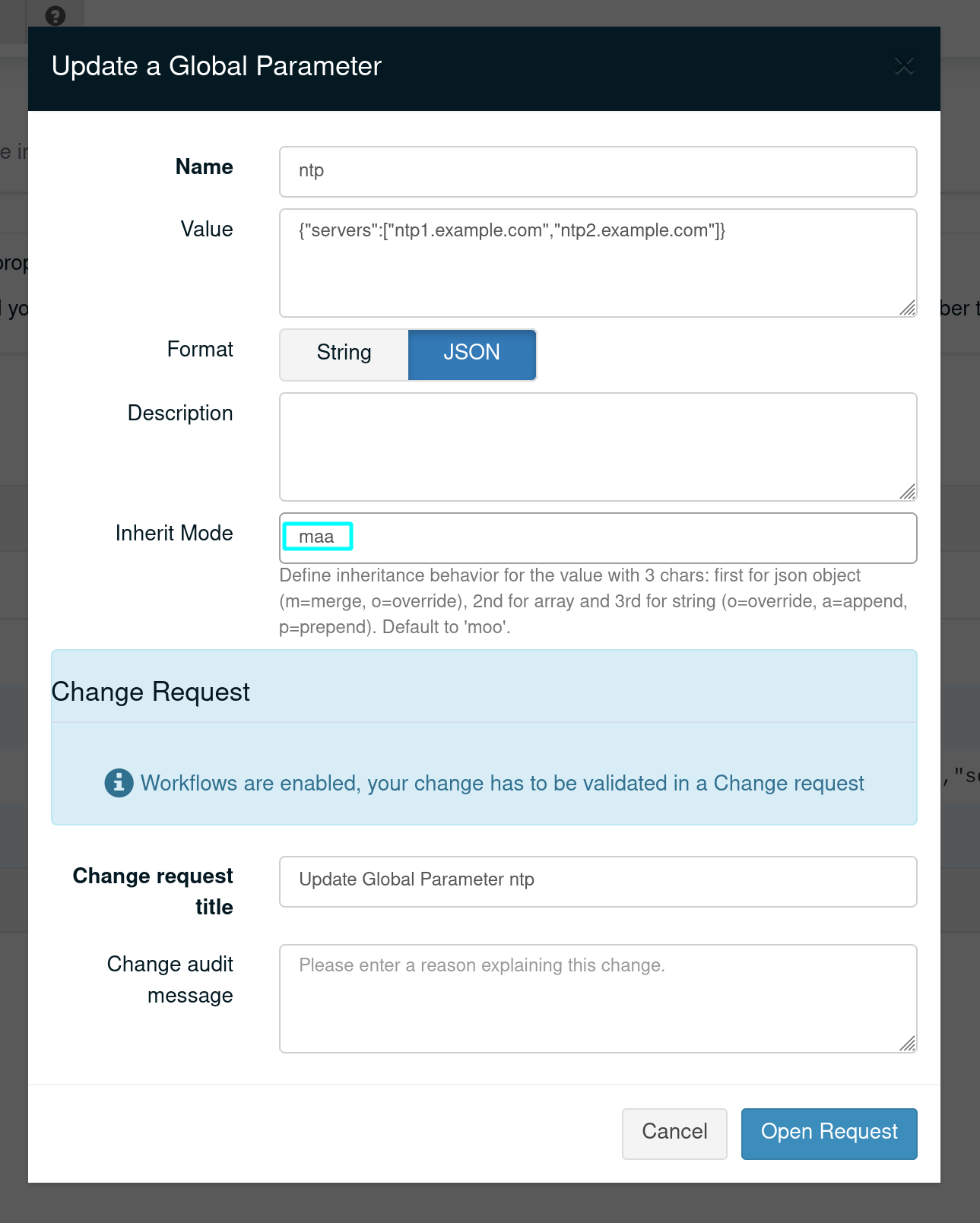
Example of setting the value for a node property to 'maa' (override object, append array and strings) via API:
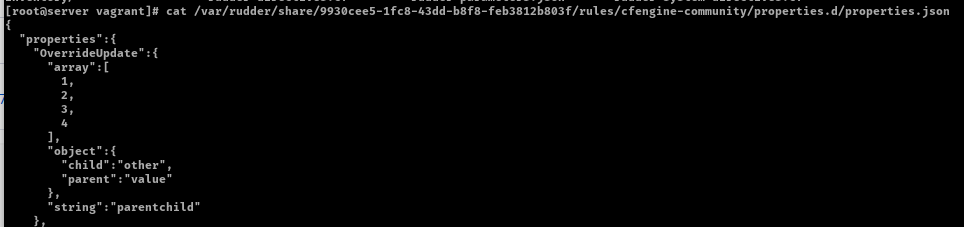
curl -X POST --header @/var/rudder/run/api-token-header -H "Content-Type: application/json" https://rudder-server/rudder/api/latest/nodes/9930cee5-1fc8-43dd-b8f8-feb3812b803f -d '{"properties":[{"name":"OverrideUpdate", "value":{"array":[3,4], "string":"child", "object":{"child":"other"}}, "inheritMode":"maa"}]}'
Result on child node properties.d directory:
Example of behavior for the default algorithm ('moo'):
// global parameter with name "example":
"example":{
"parent-kept" : "parent-kept"
, "replaced-string": "original"
, "replaced-array" : ["original"]
, "replaced-object": {"orig":"inal"}
, "replaced-array2": [1,2]
, "merge-object" : {
"parent-kept" : "parent-kept"
, "parent-replaced": "original"
}
}
// group property with name "example":
"example":{
"group-added" : "group-added"
, "replaced-string": "group"
, "replaced-array" : {"replaced":"group"}
, "replaced-object": ["group"]
, "replaced-array2": [3,4]
"merge-object" : {
"group-added" : "group-added"
, "parent-replaced": "group"
}
}
// on nodes belonging to previous group, which doesn't have "example"
// property defined (so no more overriding at that level):
"example":{
"parent-kept" : "parent-kept"
, "group-added" : "group-added"
, "replaced-string": "group"
, "replaced-array" : {"replaced":"group"}
, "replaced-object": ["group"]
, "replaced-array2": [3,4]
, "merge-object" : {
"parent-kept" : "parent-kept"
, "group-added" : "group-added"
, "parent-replaced": "group"
}
}
Global parameter
Using this, you can specify common file headers (this is the default parameter, rudder_file_edit_header), common DNS or domain names, backup servers, site-specific elements…
Rudder provides a simple way to add common and reusable variables in either plain directives, or techniques created using the technique editor: the parameters.
Group properties
Group properties can be managed by using group’s API or they can be found in the properties tab of each group in Rudder UI.
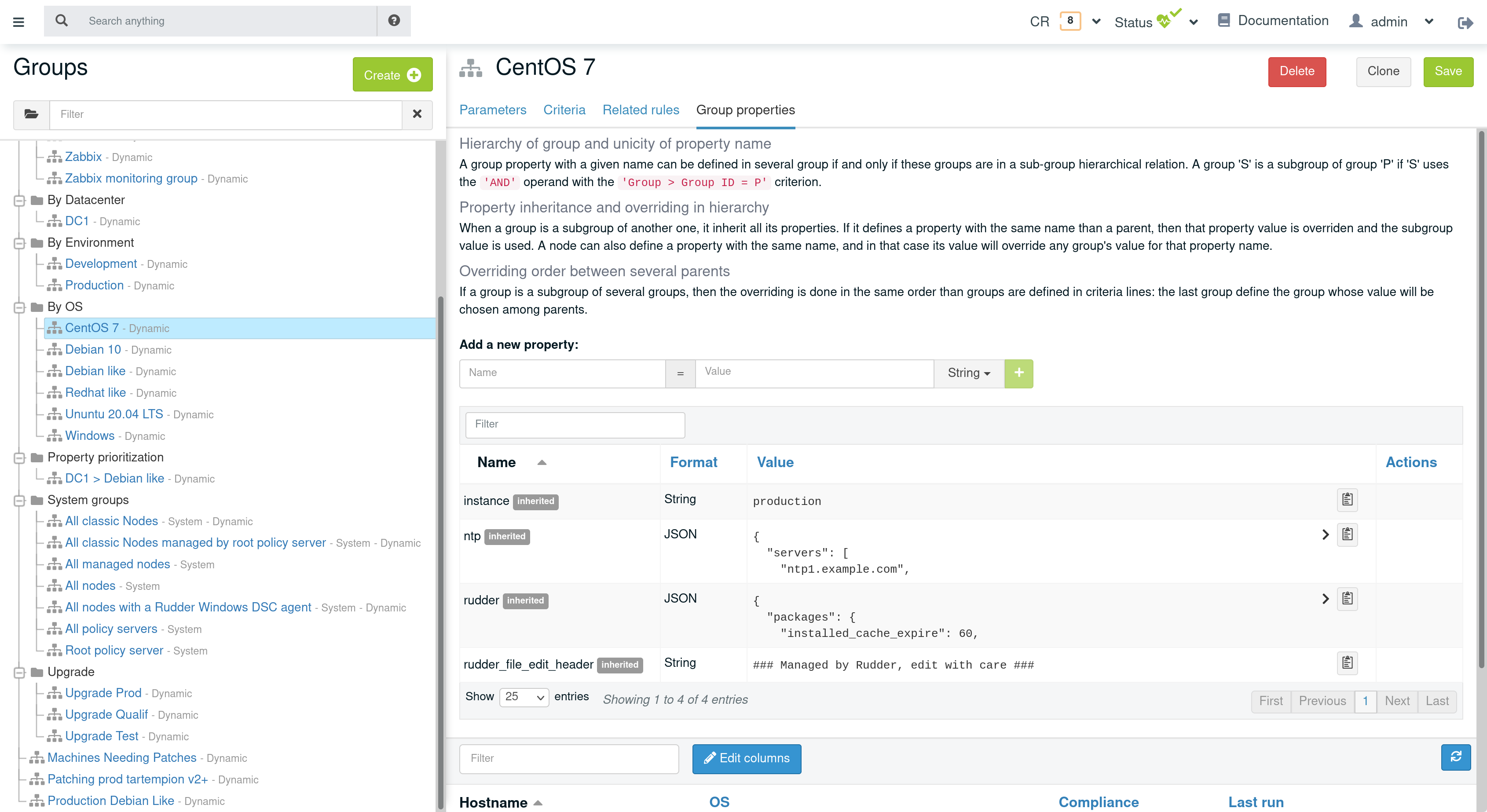
Group properties will be defined on each node that belong in that group but only when policy are generated: group properties are never actually set on nodes, which allows to override them on node and to build group from node real properties, as explained below.
Group hierarchy and property inheritance and override
Group properties are inherited and override following group hierarchy. Group hierarchy are defined by the notion of "a group S is a sub group of an other parent group `P`" defined by:
-
the subgroup
Smust have anANDcriterion operator, -
the subgroup
Smust have a criteria[Groups] [Group ID] [=] [parent group P]
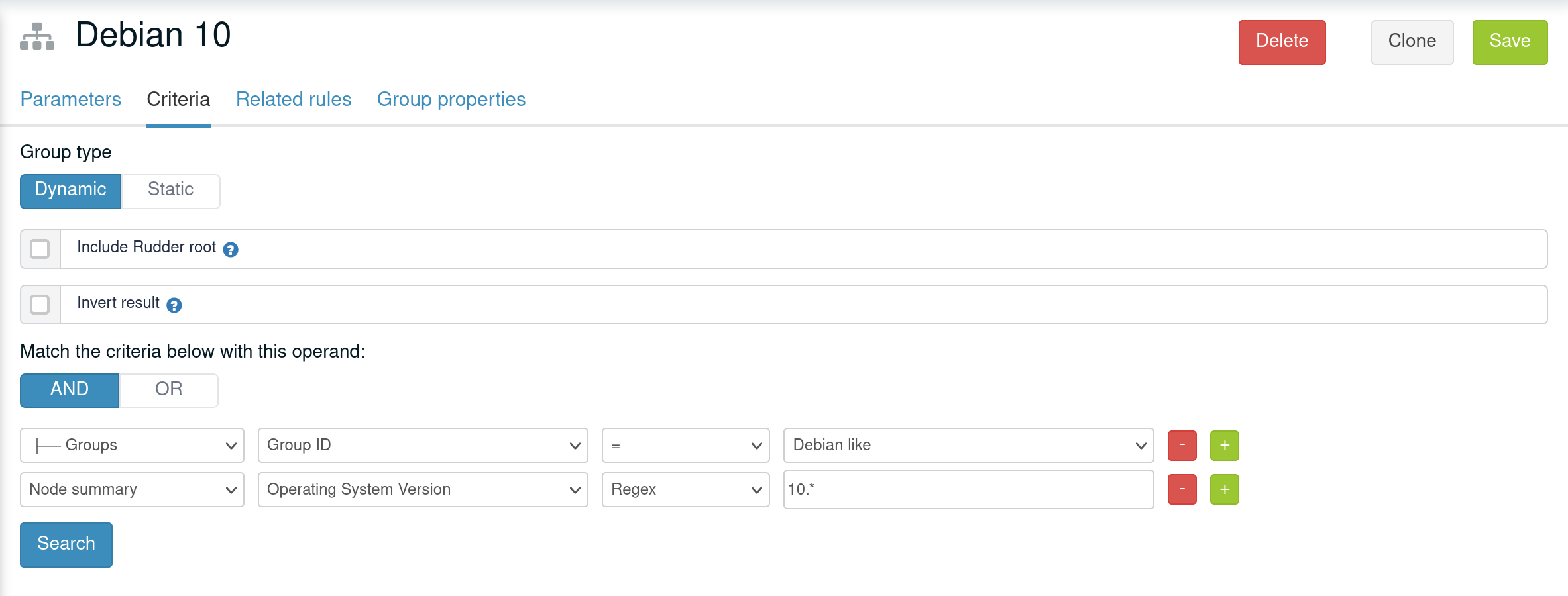
In that case, S will have all properties of P and previously explained rules for override apply.
A group can be the subgroup of several group, in which case overridden is done in criteria order (see next paragraph).
Group property conflict and prioritization
When a node inherits a property with the same name from two groups that are not in a hierarchical relation, Rudder raises an error and explains where the problem lies.
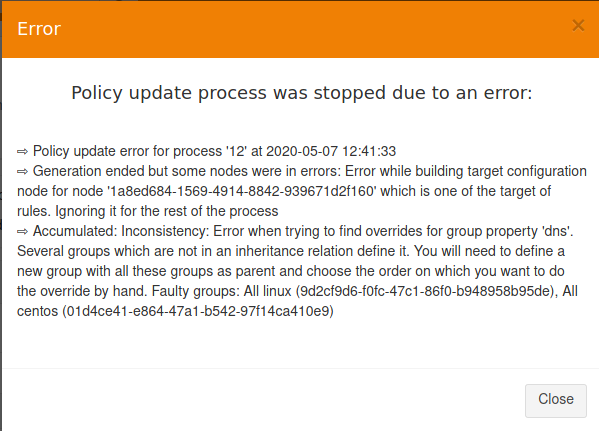
It’s important to understand that in that case, no automatic merging of properties is done because Rudder is unable to know on which way override should be done.
When such a conflict happens, you can solve it by changing the name of one of the two properties. This is the best thing to do if the properties are not really common, and the name just happened to be reused by error. Be careful that in such a case, you will also have to rename the property to the new name everywhere it’s used, which can be a bit tedious.
The other possibility is to make both group part of the same hierarchy to manually define what must be the override order. To do so, create a new group with a group criteria pointing towards each of the conflicting groups.
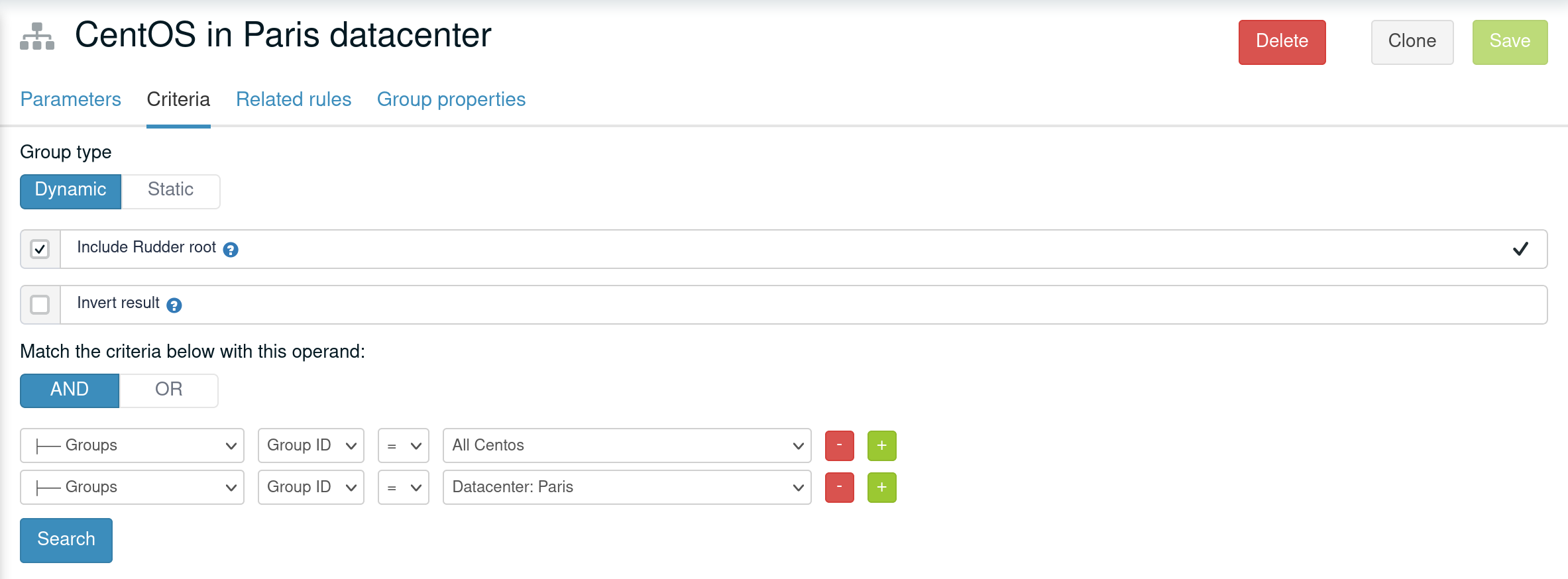
The overriding is done from first criteria line to last, so that values of group in the last line are the ones going to the node (see full example below for illustration).
Node properties used in group criteria
Rudder allows to define groups based on node properties (their existence or predicate on their value). Inherited and overridden properties are not taken into account for that definition, and only properties actually defined on nodes are used to decide if a node belongs to such a group. Doing otherwise could lead to cycles, and cycles with delay leads to oscillations, and oscillations leads to instability and chaos. We chose to remain away from the dark side, even if it brings more power.
Node properties
Node properties can be managed by using node’s API or they can be found in the properties tab of each node in Rudder UI.
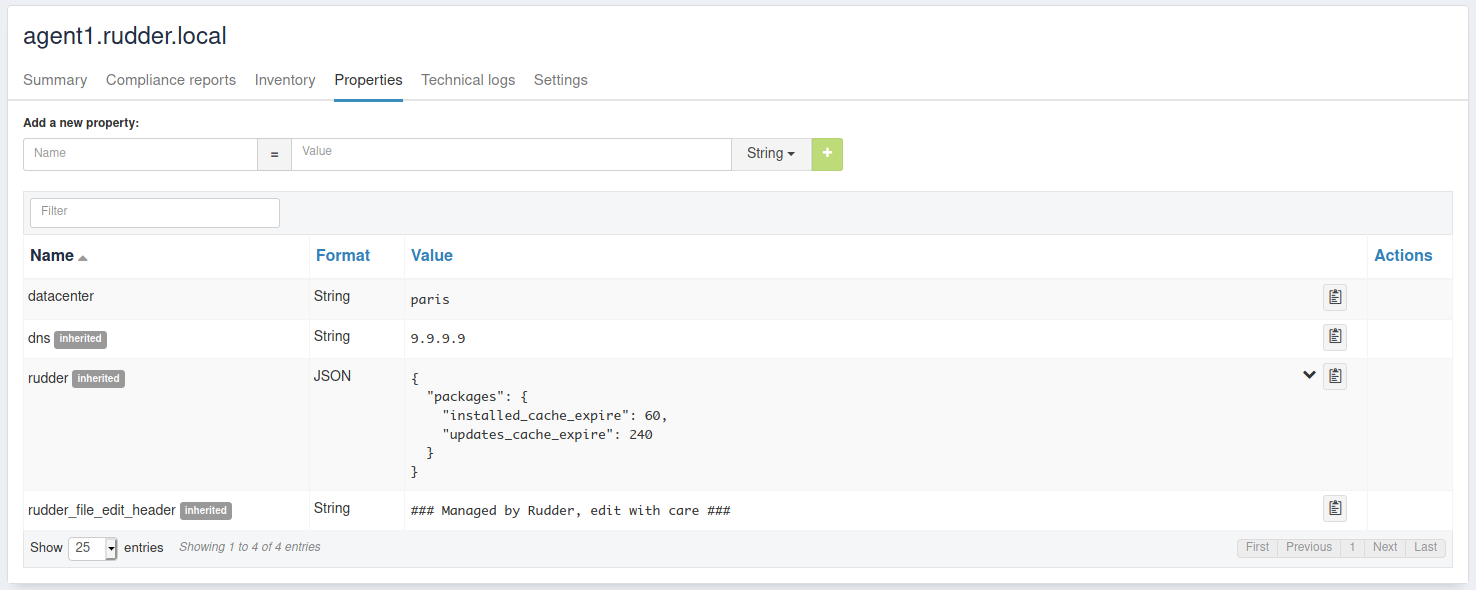
Extendable properties along the hierarchy
Properties do not have the same flexibility when creating a new property compared to when overriding a global property : the inherit mode of the global property is always kept when resolving the properties, from the top to the bottom of the hierarchy : Global > Group > Node.
This means that along the hierarchy, the behavior of appending or prepending list or string values is only possible when the highest parent overrides the global property having the inherit mode 'a' or 'p', the default value being otherwise 'o', for override. In summary, the overriding strategy along the hierarchy always depends on the behavior set for the global property, being the topmost of the hierarchy.
Therefore if you want a customisable and extendable list as property of the node (it is also possible with string values), an easy way to do it is to :
-
define a global property
propwith JSON value[], and inherit modemaoormpo(with string values, usemoaormop), -
override the property
propalong the hierarchy, for example a group A :["telnet"]and a group B inheriting A :["ssh"], and a node in B :["ftp"], -
check that the node ends up with
["telnet","ssh","ftp"]in append mode, otherwise if you want the reverse order, change to prepend mode
Configuration data example
This section provides a full example of node property definition for the following use case:
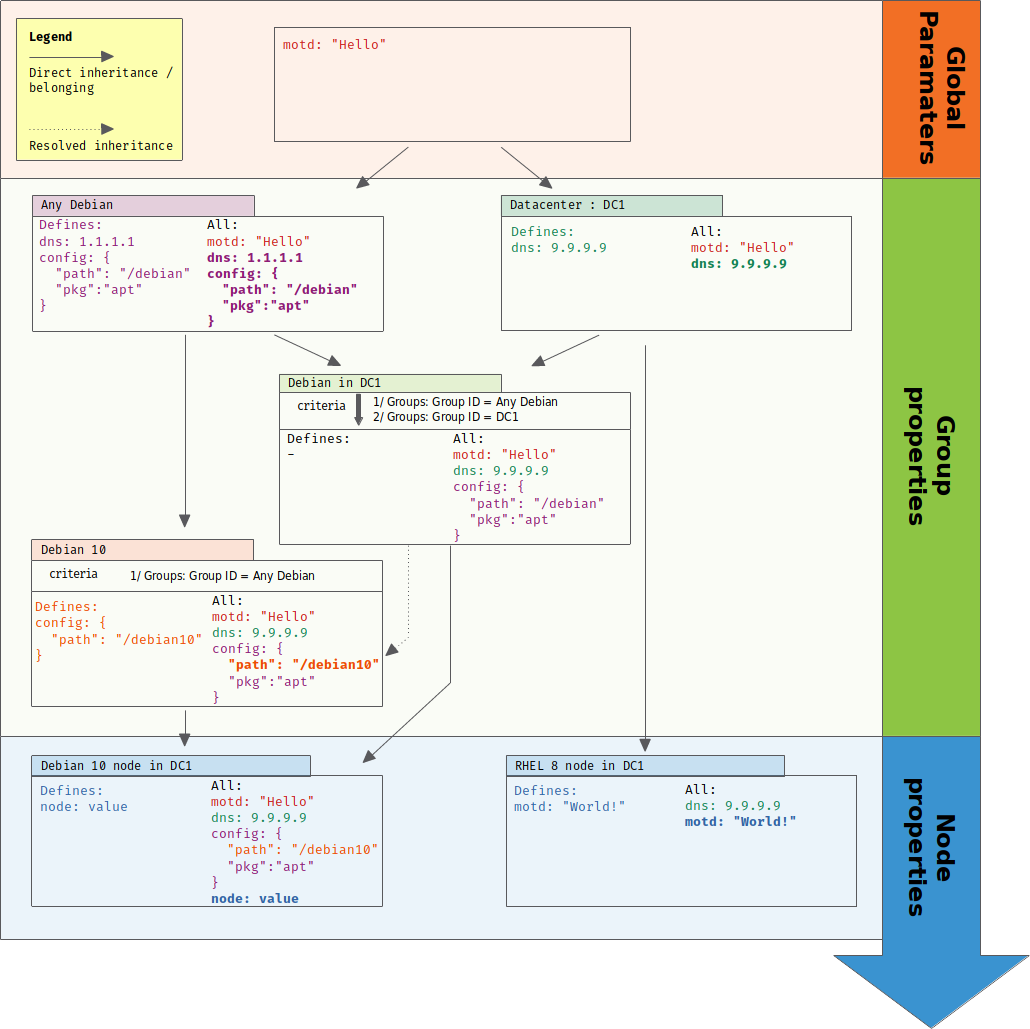
Visualizing property inheritance
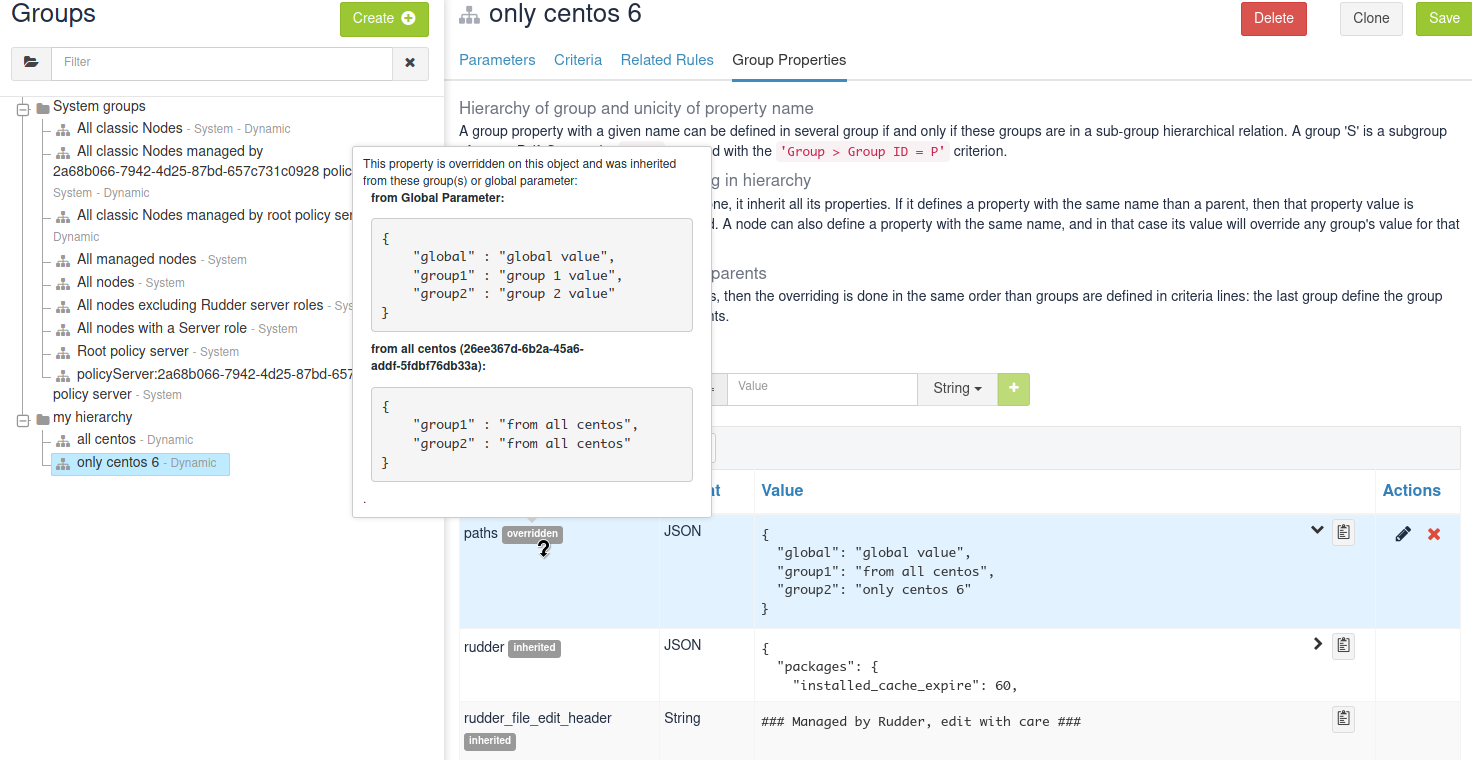
It is important to be able to understand where a property is defined and how it is overridden to be able to manage it efficiently (and more importantly, to be able to understand why it’s not what it is supposed to be).
Rudder allows to see a property lineage in group and node property tab: inherited (even if latter overridden) properties get a dedicated tag and hovering on that tag shows its full definition and overrides.
Syntax
Property syntax
| Use case | name=datacenter, value="Paris" | name=datacenter, value={"dns": "1.1.1.1"} |
|---|---|---|
Linux technique |
|
|
Windows technique |
|
|
Directive |
|
|
Mustache |
|
|
Jinja2 |
|
|
Source of environment facts
Two main cases:
-
predefined variables
-
exhaustive list: inventory variables, system variable, in the technique editor
-
-
variables acquired by code
-
read file, node local override, augeas, osquery…
-
Predefined variables and constants
Inventory variables
Inventory variables are variable whose values are coming from node inventories. They only encompass a subset of generic inventory data defined below.
If you want to use an inventory variable that you gathered through a
node inventory hook, you need to use ${node.properties[hook_first_level_key]} syntax.
You can also check in node properties tab for the name of the properties you are looking for.
|
|
These values are computed at policy generation, based on node inventory content: they may not represent current reality of the node. If you want to get facts about the node when the check is done, look at next section, especially paragraph about osquery and Augeas generic methods. |
Syntax
| Use case | name=hostname, value="Paris" | name=os, value={"name": "Debian"} |
|---|---|---|
Linux / Windows technique |
|
|
Directive |
|
|
Mustache |
|
|
Jinja2 |
|
|
Inventory variables list
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
|
Node hostname |
|
Node administrator login |
|
The architecture of the node (like "x86_64") |
|
The amount of RAM on the node (in bytes) |
|
The name of the timezone of the node (like "Europe/Paris") |
|
The operating system name (like "Debian") |
|
The operating system full name (like "Debian GNU/Linux 9.1 (stretch)") |
|
The operating system version (like "9.1") |
|
The kernel version on the node (like "4.9.0-3-amd64") |
|
The operating system service pack (like "4") |
|
The machine type (like "qemu", "physical") |
|
The manufacturer of the machine (like "innotek GmbH") |
|
The Rudder id of the node Policy Server |
System variables in directive parameters
Rudder provides system variables that contain information about nodes and their policy server.
|
You can use them only in directives and they will be expanded during policy generation. |
Since these variables are only available in directives, they are presented with the full directive-only syntax.
Information about a node:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
|
Rudder id of the node |
|
Node hostname |
|
Node administrator login |
|
The node life cycle of the node |
|
the effective policy mode of the node |
Information about a node’s policy server:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
|
The Rudder generated id of the Policy Server |
|
The hostname of the Policy Server |
|
The administrator login of the Policy Server |
Node-level system properties and constant
|
These variables are not available on Windows nodes, but only on with the Linux/AIX agent. |
| These properties are evaluated on the node at run time. |
Syntax
| Use case | name=host, value="host.local.name" | No JSON like values: name=ipv4[eth0], value=192.168.41.2 |
|---|---|---|
Linux technique |
|
|
Windows technique |
N/A |
N/A |
Directive |
|
|
Mustache |
|
Be careful! System variables like
|
Jinja2 |
|
Be careful! System variables like
|
System property
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
Kernel short architecture |
|
Fully qualified hostname, as seen in Rudder |
|
Unqualified hostname |
|
Node’s hostname (according to the kernel) |
|
Node’s domain as discovered by the agent |
There are also more variables available, all documented in this page.
Node environment information at run time
Often, you will need to capture values from the node context when the agent runs. It may be because you need to access information only relevant or defined on the node, like current open ports, because the information is only reachable from it like a REST API open only for node subnet, or for security reasons like providing secrets only to the node. Rudder provides a range of possibilities to cover these use cases.
Automatic loading of JSON variable
All files with .json extension placed in /var/rudder/local/properties.d/ are loaded as variable with JSON values for each agent run. For these files, the root level JSON keys are used as variable name prefix, the second level keys are used as variable names and following levels are used as value.
For example, the following file:
{
"prefix1": {
"stringVar": "value1",
, "jsonVar": {
"moreLevel":"levels"
}
}
, "prefix2": {
"stringVar": "value2"
}
}
will define three variables:
-
${prefix1.stringVar}with valuevalue1, -
${prefix1.jsonVar}with value{"moreLevel":"levels"}`, -
${prefix2.stringVar}with valuevalue2,
Node property local override
Node properties can also be defined directly on the nodes, by creating properties files in /var/rudder/local/properties.d/*.json. File will be read in read in alphabetical order and any variable under the root key properties will be considered to be a node property
|
Existing node properties will be replaced and not merged by properties with the same names in node local override. If you want to merge properties, you will need to define them with different name and merge them by hand (see below). |
As a result, if you have server-side node properties as
"sysctls_postgresql":{"kernel.shmall":"903330","kernel.shmmax":"3700041320"} and
"vm":{"vm.dirty_ratio":"10"}
and a local property file /var/rudder/local/properties.d/postgresql_config.json as
{
"properties":
{
"sysctls_postgresql": {
"kernel.shmmax":"5368709120"
}
}
}
The resulting properties will be:
"sysctls_postgresql":{"kernel.shmmax":"5368709120"} and
"vm":{"vm.dirty_ratio":"10"}
sysctls_postgresql has been replaced by local property, and vm has been left untouched.
Variable defined by agent
Agents can define variables:
-
For the Linux agent, CFEngine system variable are available.
-
For the Windows agent, no specific variables are provided.
Variable defined from techniques and generic methods
Rudder provides a set of generic methods (and techniques) that allows to define variables from a wide range of inputs. For each case, the generic method reads a source of information and translates it into a Rudder variable for which you provide a prefix and a name.
Rudder also provides techniques similar to generic methods that allow to define variables from string, json, or command output.
In most case, it’s easier to use generic methods as they allow to:
-
group several variable definitions in the same place
-
encapsulate variable definition and usage in the technique, avoiding dependencies between directives (which should be avoided as much as possible).
We present afterward a subset of interesting cases, but there is others that you can check out in generic method documentation.
Variable override by order of rules and directives
Variables defined with following generic methods or corresponding techniques can be overridden by other variables with same name defined in other rules or directives.
The exact ordering and rules are explained in the ordering directive chapter.
It is not recommended to rely on this mechanism as dependencies between directives are not easily visualizable.
Variable from files
Rudder can natively parse JSON, YAML and CSV files to transform them into JSON values.
Variable from Augeas
Augeas is a standard tool for reading and editing configuration files by providing a tree-representation of their native format. It’s really useful to clean the mess in that domain. With it, you can easily and safely transform almost any configuration file into a Rudder JSON variable.
Variable from osquery
osquery is a tool that allows to query information about your system through SQL-like queries. It’s becoming a de-facto standard, and with it you can get an accurate, real-time glimpse of your node and put that data into a Rudder JSON variable.
Variable from Vault
Vault is becoming a de-facto tool to securely share secrets in a complex infrastructure, when your attack vector and mitigation includes having different people configuring systems and setting secrets. Rudder provides a generic method through a plugin to access a Vault secret and use it in a configuration only locally from the node.
Variable from command
In last resort, you can always write a script to get what information you want, format the corresponding data in JSON and define a variable from that. This is especially useful when you need to retrieve data from a REST endpoint at run time - but beware of the implied latency on each run!
Merging variable’s values
With all these variables coming from different sources, you will likely need to consolidate values on the node by creating overridden values.
Rudder provide two generic methods to merge values:
-
variable_dict_mergewill replace properties with the same name, -
variable_dict_merge_tolerantwill merge properties with the same name.
This second method can be used if you want to merge server defined properties with local defined properties rather than replace them. For that, define the node local variables in a different namespace than properties.
For instance, if the following node properties was defined:
"sysctls_postgresql":{"kernel.shmall":"903330","kernel.shmmax":"3700041320"}
You can define a file /var/rudder/local/properties.d/postgresql_config.json with the following content:
{
"local_properties":
{
"sysctls_postgresql": {
"kernel.shmmax":"5368709120",
"kernel.shmmni":"4096"
}
}
}
and use the generic method variable_dict_merge_tolerant to merge node.properties[sysctls_postgresql] and node.local_properties[sysctls_postgresql], and set the result in merged_properties.sysctls_postgresql (for instance): variable_dict_merge_tolerant("merged_properties", "sysctls_postgresql", "node.properties[sysctls_postgresql]", "node.local_properties[sysctls_postgresql]")
As a result, merged_properties.sysctls_postgresql will contain
"sysctls_postgresql": {
"kernel.shmall":"903330",
"kernel.shmmax":"5368709120",
"kernel.shmmni":"4096"
}
Using variables
Technique vs directive vs template
There’s little use defining variables if you don’t use them. In this section, we will explain the three main use cases of variables with their particularities:
-
variable used in techniques, i.e. in code designed to run on agent (and sometimes even only for a specific agent); here we deal with data used to lead logic (condition or iteration on set of data, etc).
-
variable in templates are a special cases of previous case: they are expanded on node, during agent run. But their syntax and usage are directed by the template engine,
mustacheorjinja2in Rudder; -
on the other hand, variables in directives parameters are likely only configuration data defined elsewhere and used to parameterized a technique used as a configuration template. Variables in directive are generally expanded during policy generation in the policy server, and most errors can be caught at that time.
The next paragraph will detail specificities of each case.
Technique
In Rudder, you can define and use variables via the technique editor or the different pre-built techniques. If you happen to write your own generic methods, variables in them follow the same rules.
All variables are defined under a prefix (scope), so to reference a variable you will always need its prefix and its name, separated via a . char.
To call a variable in Rudder we use ${…} brackets syntax as described below:
For backward compatibility, the syntax $(…) is also supported, but deprecated and not recommended.
|
// Call to a String or Iterator variable
${<prefix>.<variable name>}
// Call to a key in a Dict variable
${<prefix>.<variable dict name>[key][sub-key]}
In techniques, variables can be of one of three types:
-
A
String -
A
Dict, which support key-values and arrays, i.e. JSON like structure, -
Or an
Iteratorwhich is used to loop over things in Rudder.
More over, all variables in Rudder are overridable at execution time, keep in mind that ordering the definition of your variables is important.
Technique parameters
Technique parameters can be referenced with the following syntax:
# Variable corresponding to a technique parameter, full version:
${technique_id.parameter_name}
The complete parameter name is mostly used to access the parameter value from a template or when using method which takes a variable name as argument such as condition_from_variable_match.
But since they are local to each technique, you can often reference them by eliding the technique_id part:
# Variable corresponding to a technique parameter, short version:
${parameter_name}
Conditionals
Conditions concept in Rudder
Conditions in techniques are a bit different than your regular booleans in a programming language. Their first use case is to control execution of a generic method and so they are better understood as guards: if a set of predicates on that guard is verified, then the generic method is executed, else a report not applicable (N/A) is generated.
A condition is represented by a string, and can be either defined or not. The conditions express what the current execution environment is:
-
We are on a Debian 9 system
-
The state of the nginx package is correct
-
The content of the configuration file has just been modified
-
etc.
the string that define a condition is often called a class - not in the object oriented programming meaning, but in the categorization one.
|
We can use conditions to limit the evaluation of a method to a specific context, for example only on debian 9 or only when a given file has been modified by the agent.
This allows: - using actions (like service restart) by limiting them to a specific context - writing generic policies compatible with different operating systems, by having specific parts for each
| if you need to code some complex logic with lots of branching (i.e. lots of interlocked if/then/else, or even recursive conditions), then it will be hard to do so at technique level. It is likely that complex logic should be encapsulated in an idempotent script, or even factored-out in a new generic method. |
Conditions can be combined using boolean operators:
-
!for not -
|for or -
.for and -
(and)for grouping
This is an example about how to define two generic methods, one for installing python3-jinja2 on CentOS 8 (with the predefined OS form, which is the preferred solution), and one for installing python-jinja2 on CentOS 6 and 7 (with the OS system variable (see below) and negation operator, for demo):
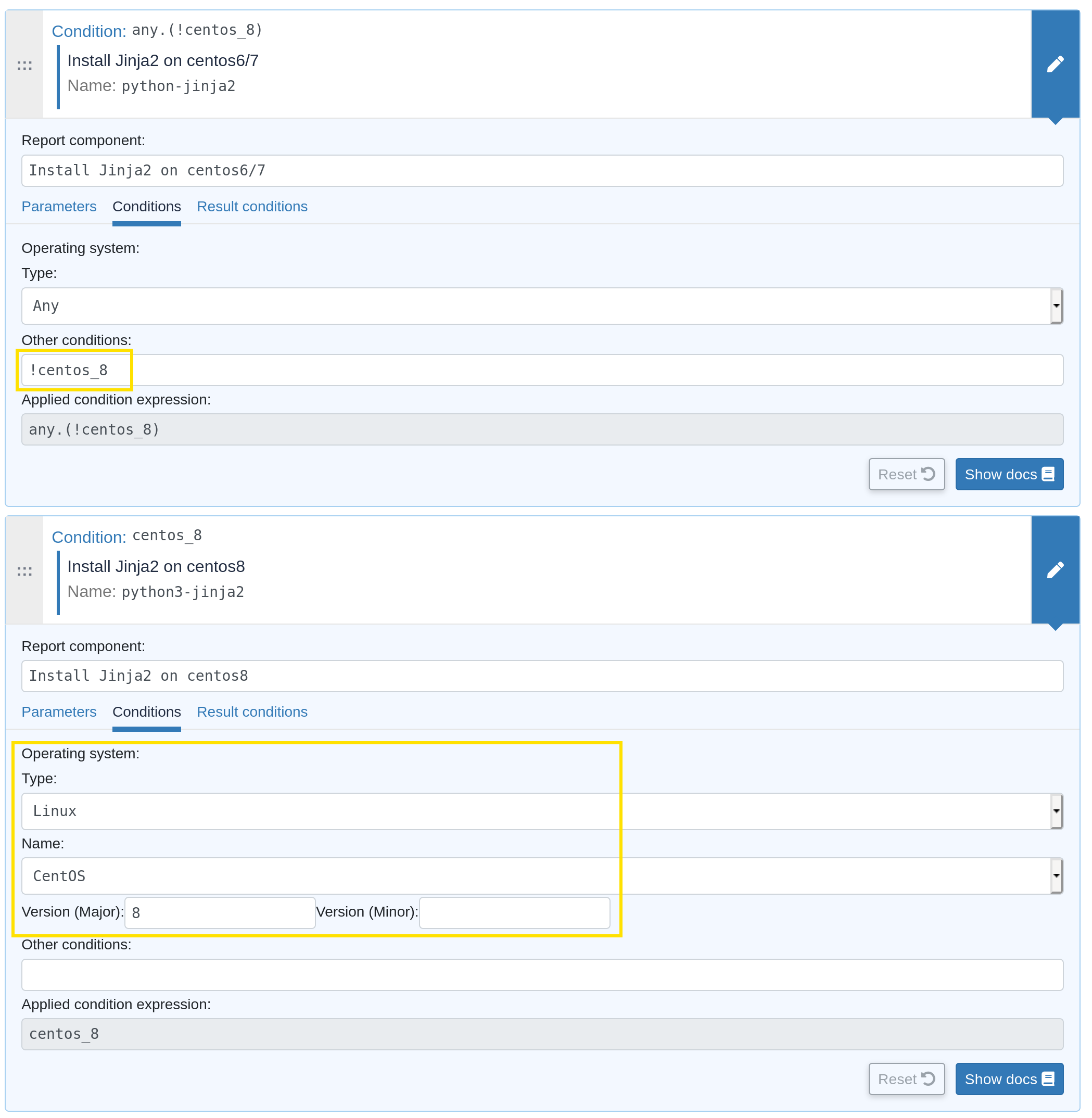
Automatically defined condition classes
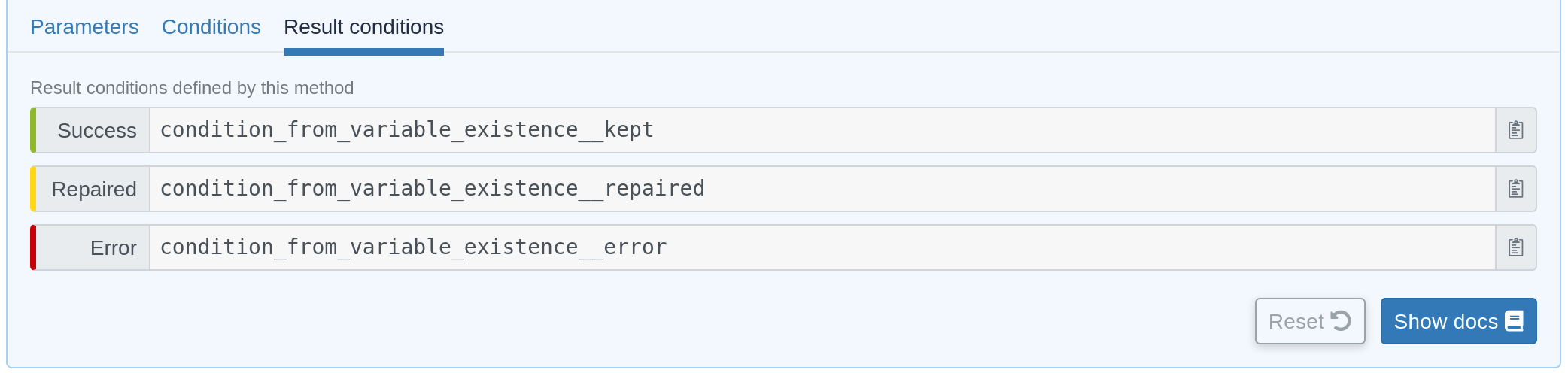
Generic method result
Every method will define a result condition that is one of the conditions displayed in method details:
It can be:
-
Success: When the state was already compliant
-
Repaired: When the state has been modified by the agent to become compliant
-
Error: When the expected state could not be reached
Group
Group conditions are defined only if the node is in the given group (available in the group details):
-
group_[group_uuid] -
group_[group_name]
System conditions
In the same spirit that some variables are defined by default when the agent runs, a set of condition is defined based on the environment execution context. These conditions cover mainly information about the system (os, etc) and information about time.
These conditions are different on each agent, and of course on each run depending on the context. You can see which one are defined by executing the following command on your node:
rudder agent info -v
On Linux agent, you can also start a run with some defined condition with the command:
rudder agent run -D my_condition
Time classes (available on all agents)
| Description | Names |
|---|---|
Day of the Week |
|
Hour of the Day in Current Time Zone |
|
Hour of the Day in GMT |
|
Minutes of the Hour |
|
Five Minute Interval of the Hour |
Note the second number indicates up to what minute the interval extends and does not include that minute. |
Quarter of the Hour |
|
An expression of the current quarter hour |
|
Day of the Month |
|
Month |
|
Year |
|
Period of the Day |
|
Lifecycle Index |
|
Linux agent (non exhaustive list)
| Description | Names |
|---|---|
Always set conditions |
|
Never set condition |
|
Operating System Architecture |
|
VM or hypervisor specific |
|
On Solaris-10 systems, the zone name |
in the form |
Windows agent
| Description | Names |
|---|---|
Always set class |
|
Operating System Architecture |
|
| In Windows agent, classes are defined in that source file. |
Condition classes from code
Rudder provides several methods to define conditions from code. They are explained in the corresponding generic methods documentation and cover three main use cases:
-
condition from expression, which defined new condition classes by combining existing condition classes,
-
condition from variable, which allows to define a class based on the existence of a variable or based on predicate upon its value,
-
condition from command, which is the swiss-knife to use when you want to test anything about anything.
Iterations
As for conditionals, iterations in Rudder are not your well known programming language for-loop.
Iteration are used to apply some configuration logic to a list of elements without wondering about the low-level aspects of how the iteration is done.
You build an iterator either from a JSON variable or a file. You never explicitly iterate over it, you just reference the fields of the iterated item in following generic methods.
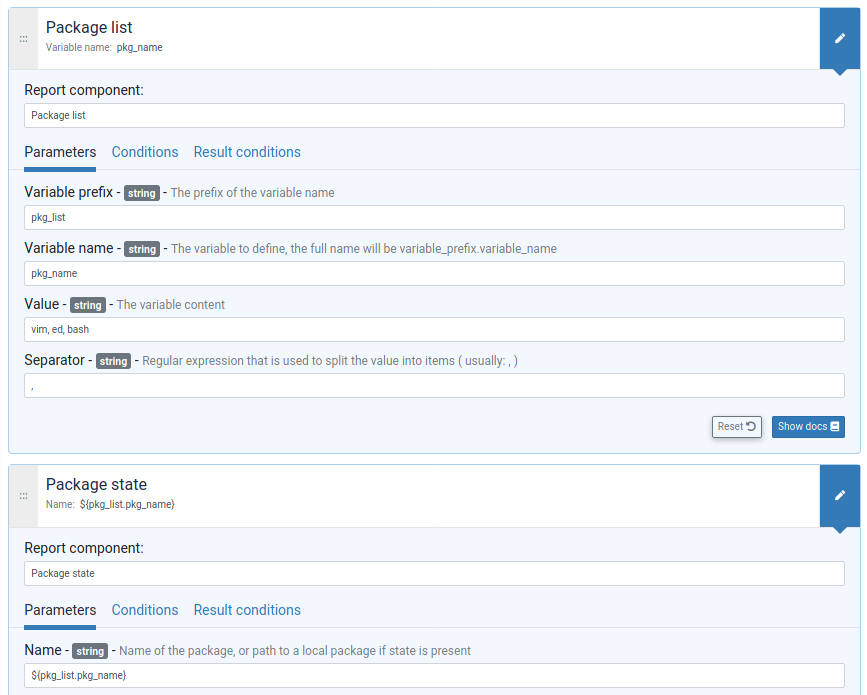
File content: templates and edition
A non negligible part of configuration management is filing template files with values and using that. In Rudder, we provide three main ways to do that:
-
the first fulfills simple use cases, like lightly editing a file, or copying from a reference and is available through
file contenttechnique and generic method, -
the second, focused on configuration file edition, is available through
Augeastools already presented for variable definition, -
the last, which covers involved file edition with possibly logic and loops, can be achieve through full-fledged template engine. Rudder natively provides two of them:
Jinja2andMustache.
File edition technique and generic methods
Rudder provides a swiss-knife file edition technique, File Content that allows to do a lots of thing like:
-
checking for file existence and permission,
-
ensuring that the file exactly matches a reference content,
-
ensuring lines are present or absent,
-
checking that part of file exists by section,
-
enforce content by section.
Directive from that technique can become quite complex and most of the time, defining idempotent changes in files through regex is hard. This is specially true when several checks from that technique are used in conjunction.
When it’s possible, we advice to either use more atomic generic method to build your own simpler change, or even better to default to either Augeas for configuration file edition or a template engine for ensuring file content (see below).
Augeas
Augeas is not exactly a full-fledged template system but its primary goal is also to define values in files, and in the domain of configuration management it is a very common use case.
Augeas is not embedded in rudder agent and will need to install it on nodes before using it.
You can execute Augeas commands through corresponding generic methods.
Mustache
Mustache is a simple template engine that allows to expand variables but does not support heavy logic or data transformation.
Mustache is embedded in rudder agent and you don’t need to install anything on nodes to use it.
Conditions:
{{#classes.condition}}
condition is defined
{{/classes.condition}}
{{^classes.condition}}
condition is not defined
{{/classes.condition}}
Variables:
{{{vars.node.properties.variable_name}}}
{{{vars.generic_variable_definition.variable_name}}}
{{{vars.variable_prefix.string_name}}}
{{{vars.variable_prefix.dict_name.key}}}
Iterations:
{{#vars.variable_prefix.iterator_name}}
{{{.}}} is the current iterator_name value
{{/vars.variable_prefix.iterator_name}}
{{#vars.variable_prefix.dict_name}}
{{{@}}} is the current dict_name key
{{{.}}} is the current dict_name value
{{/vars.variable_prefix.dict_name}}
{{#vars.variable_prefix.dict_name}}
{{{.name}}} is the current dict_name[name]
{{/vars.variable_prefix.dict_name}}
You can read a full example of file template in Rudder by example.
Jinja2
Jinja2 is a full-featured Python template engine that supports anything you can imagine from a template engine, but with the corresponding complexity.
Jinja2 is not embedded in rudder agent. You will need to install it by yourself on nodes where you want to use it (and of course you can use rudder for that!).
Conditions:
{% if classes.condition is defined %}
condition is defined
{% endif %}
{% if not classes.condition is defined %}
condition is not defined
{% endif %}
Variables:
{{ vars.variable_prefix.my_variable }}
Iteration:
{% for item in vars.variable_prefix.dict %}
{{ item }} is the current item value
{{ item.key }} is the the current item[key] value
{% endfor %}
{% for key,value in vars.prefix.dict.items() %}
{{ key }} has value {{ value }}
{% endfor %}
More information about loops and other control structures is available in Jinja2 template documentation.
You can read a full example of file template in Rudder by example.
Directive
Variables can be used in directives where technique parameters are defined. These variables are expanded for each node during policy generation and checks are done at that moment, like if the variable is correctly defined.
You should always prefer to use node properties with global parameter and group properties inheritance to define such parameters for configuration data and keep variable from generic methods or technique for information only available on the node at run time.
Node properties expansion in directives
In any directive text field, you can access properties defined on nodes using the following syntax:
${node.properties[property_name][key_one][key_two]}
where:
-
property_nameis the name of the property defined via the API -
key_oneandkey_twoare keys in the JSON structure -
the value obtained is the string representation, in compact mode, of the entire node property or sub-structure of the JSON value
-
if the key is not found, an error will be raised that will stop policy generation
-
spaces are authorized around separators (
[,],|,}..)
Providing a default value in directives
You may want to provide a default value to node properties expansion to avoid a policy generation error due to missing node properties. This is also a good case to allow a simple override mechanism for a parameter where only some nodes have a specific value.
You can also use other node properties, or other Rudder parameters as defaults, using the same syntax as above.
This syntax is not available in Technique Editor. The preferred method in Technique Editor is to use the Variable String with Default generic method, or use a Technique Parameter.
|
Default values must quoted with double quotes ("…“) or triple double quotes (”""…"""). You can omit quotes in the case where the default is only composed of exactly one variable.
Some examples:
${node.properties[datacenter][id] | default = "LON2" }
${node.properties[datacenter][name] | default = """Co-location with "Hosting Company" in Paris (allows quotes)""" }
${node.properties[datacenter][id] | default = "${rudder.properties[default_datacenter]} }"
${node.properties[netbios_name] | default = "${rudder.node.hostname}" }
${node.properties[dns_suffix] | default = ${node.properties[datacenter][dns_suffix] | default = "${rudder.node.hostname}.example.com" }
#or even use cfengine variables in the default
${node.properties[my_override] | default = "${cfengine.key}"}
Forcing expansion on the node
In some cases, you will want to use a ${node.properties[key]} in a directive parameter, but you don’t want to expand it during
policy generation on the Rudder server, but instead let the value be expanded during the agent run on the node. This typically happens if the value can be overridden on the node.
For these cases, you can add the "node" option to the property expression:
${node.properties[datacenter][id] | node }
This will be rewritten during policy generation into:
${node.properties[datacenter][id]}
Which will be considered as a standard variable by the agent, which will replaced this expression by its value if it’s defined, or kept as is if it’s unknown.
The variable content is read from /var/rudder/cfengine-community/inputs/properties.d/properties.json, and from the optionally defined /var/rudder/local/properties.d/*.json files.
You can find more information on node properties in node properties documentation.
JavaScript evaluation in Directives
It is possible to use javascript expressions to build directive values. The
resulting values will be computed during policy generation, and can therefore
provide unique values for each node.
Switching feature availability
You can disable this feature in the Administration/Settings page, using the Enable script evaluation in Directives parameter.
Usage
All standard JavaScript methods are available, and a Rudder-specific
library, prefixed with rudder. also provides some extra utilities. This
library is documented below.
For example, to get the first 3 letters of each node’s hostname, you can write:
"${rudder.node.hostname}".substring(0,3)
|
Limitation of the scripting language
JavaScript expressions are evaluated in a sandboxed JavaScript environment. It has some limitations, such as:
|
Rudder js utility library
Standard hash methods
The following methods allow to simply hash a value using standard algorithms:
-
rudder.hash.md5(string) -
rudder.hash.sha256(string) -
rudder.hash.sha512(string)
These methods do not use a salt for hashing, and as such are not suitable for distributing passwords for user accounts on UNIX systems. See below for a preferable approach for this.
UNIX password-compatible hash methods
The following methods are specially designed to provided hashes that can be
used as user passwords on UNIX systems (in /etc/shadow, for example). Use
these if you want to distribute hashes of unique passwords for each of your
nodes, for example.
Two different cases exist: support for generic Unix-like systems (Linux, BSD, …) and support for AIX systems (which use a different hash algorithm).
Available methods are:
-
rudder.password.auto(algorithm, password [, salt]) -
rudder.password.unix(algorithm, password [, salt]) -
rudder.password.aix(algorithm, password [, salt])
The parameters are:
-
algorithmcan be "MD5", "SHA-512", "SHA512", "SHA-256", "SHA256" (case insensitive) -
passwordis the plain text password to hash -
saltis the optional salt to use in the password (we strongly recommend providing this value - see warning below)
The unix method generates Unix crypt password compatible hashes (for use on
Linux, BSD, etc), while the aix method generates AIX password compatible
hashes. The auto method automatically uses the appropriate algorithm for
each node type (AIX nodes will have a AIX compatible hash, others will
have a Unix compatible hash). We recommend always using auto for simplicity.
For example, to use the first 8 letters of each node’s hostname as a password, you could write:
rudder.password.auto("SHA-256", "${rudder.node.hostname}".substring(0,8), "abcdefg")
|
Providing a salt
It is strongly recommended to provide a salt to the methods above. If no salt is provided, a random salt is created, and will be recreated at each policy generation, causing the resulting hashes to change each time. This, in turn, will generate an unnecessary "repaired" status for the password component on all nodes at each policy generation. |
Status and future support
In a future version of Rudder, JavaScript evaluation will be supported in all fields in Directives, including non plain-text fields.
In the meantime, you can already test this functionality out by entering a JavaScript
expression in any Directive field, prefixed by evaljs:. Please be aware that
this is unsupported and untested, so do this at your own risk.
There is currently no plan to extend this support to the fields in the Technique editor.
Auto-conditions
If you need to define classes based on the value of properties for your policy, auto-conditions are a nice feature avoiding to having to define the conditions manually in the techniques. This allows easily taking advantage of the inheritance and merge mechanisms of the properties directly in your techniques.
Define auto-conditions
The feature is enabled by defining a rudder_auto_conditions JSON property
containing an array of strings. The strings are the names of the property to enable
the auto-conditions for.
Use auto-conditions
Once enabled, the auto-conditions expect a specific data structure, and the properties that will be translated to conditions have to be an object (containing key-value pairs) with either string or boolean values.
-
If the value is a boolean
-
If the value is
true, the${variable_name}_${key}condition will be defined -
If the value is
false, nothing happens
-
-
If the value is a string
-
the
${variable_name}_${key}_${value}condition is defined
-
-
If the value has any other type, nothing happens
-
If the property is not defined, nothing happens
Example
Define rudder_auto_conditions TO ["myautocond"].
Then you can define the myautocond property (at any level, and using
the override and merge features), giving on the node level:
{
"choice": "A",
"enable_policy": true,
"enable_purge": false
}When your agent runs, it will define before running any policy the conditions:
-
myautocond_choice_A -
myautocond_policy
← Technique editor Advanced configuration management →