Advanced configuration management
Policy generation
Each time a change occurs in the Rudder interface, having an impact on the policy needed by a node, it is necessary to regenerate the modified policies for every impacted node. By default, this process is launched after each change.
The process of policy generation:
-
Use configured policies and information about the nodes to generate the files defining the policy that reflects the desired state
-
Compute and store expected reports that will be produced when executing these policies
-
Check the validity of the generated policies
-
Replace the old version of the policies by the new one for impacted node
-
Restart the policy server on the Rudder central server is authorizations have changed
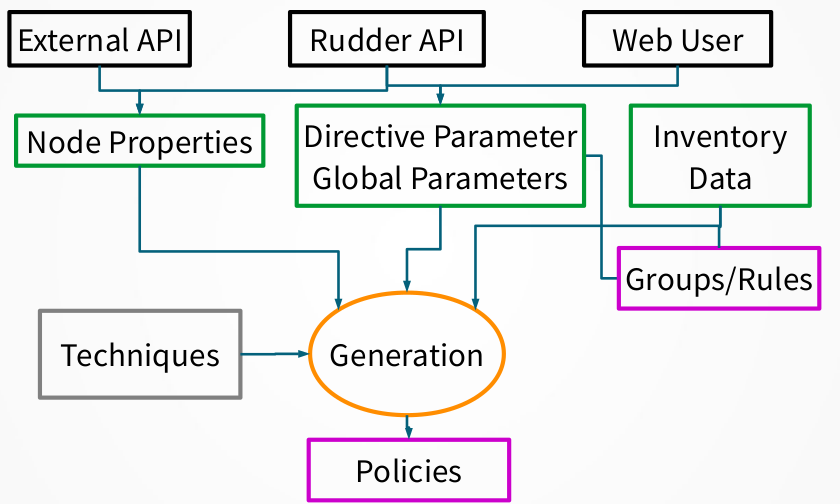
You can customize some of these actions and add new ones using the Server Event Hooks.
Update policies button
The button Update policies on the top right of the screen, in the Status menu, allows you to force the regeneration of the policies. As changes in the inventory of the nodes are not automatically taken into account by Rudder, this feature can be useful after some changes impacting the inventory information.
Regenerate all policies button
The button Regenerate all policies on the top right of the screen, in the Status menu, allows you to force the regeneration of all policies. It will clear all internal caches, and force a complete computation of the policies. This is generally useful to make sure everything is correct after a problem on the central server.
Policy generation info log
Policy generation is a complex process, and it is central to Rudder use. You will often want to know more about a policy generation result: what was the reason for a failure? What nodes where updated? Or even more specific info like: where are info and debug log?
/var/rudder/policy-generation-info
Directory /var/rudder/policy-generation-info contains information about the last policy generation(s)
in the following files:
-
last-failure-message: when a generation fails, failure message is stored here. It is helpful for debugging purpose (for example when message is very long), or to know what happened in case of transient errors. -
last-updated-nodeids: this file contains list of node updated in last generation. It is in a source-able format which defined three bash array: -
RUDDER_UPDATED_POLICY_SERVER_IDS: contains the set of updated policy servers (root or relay) -
RUDDER_UPDATED_NODE_IDS: contains the set of updated standard nodes -
RUDDER_NODE_IDS: contains both updated policy server and nodes. Policy servers always come first.
Each file starts with a comment describing what policy generation generated it.
Two version of each of these files is conserved: the oldest one has a .old suffix.
webapp logs
Rudder web application logs located in /var/log/rudder/webapp/webapp.log contains information
about policy generation process. All policy generation logs are gathered under policy.generation
namespace (with optionally more precise namespace, like policy.generation.timing for timing information, or
policy.generation.update for updated nodes, etc).
By default, policy generation logs when it starts with generic information about system:
[2020-03-12 15:32:28+0100] INFO policy.generation - Start policy generation, checking updated rules [2020-03-12 15:32:29+0100] INFO policy.generation - [metrics] Xmx:1.55 GB nodes:8 (cached:0) rules:248 (enabled:35) techniques:131 (enabled:127) directives:238 (enabled:224) groups:26 (dynamic:17) parameters:3
How many nodes were updated:
[2020-03-12 15:32:39+0100] INFO policy.generation - Configuration of 8 nodes were updated, their policies are going to be written
Timing information about generation steps (they are always logged to allow checking general performance evolution):
[2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Timing summary: [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Run pre-gen scripts hooks : 200 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Run pre-gen modules hooks : 19 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Fetch all information : 325 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Historize names : 7004 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Build current rule values : 327 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Build target configuration : 2277 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Write node configurations : 57132 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Save expected reports : 80 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Run post generation hooks : 411 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Number of nodes updated : 8 [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Policy generation succeeded in: 1 min 9 s
End finally summary of generation: success or failure, total time:
[2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation - Successful policy update '10198' [started 2020-03-12 15:32:28 - ended 2020-03-12 15:33:37]
Much more information can be logged about policy generation (hook execution and timing, much more precise timing,
updated nodes, files written, etc). All corresponding logs and verbosity levels are documented and controlled
in /opt/rudder/etc/logback.xml.
Server Event Hooks
Files (hooks), typically scripts, can be executed on the server, when some predefined event occurs on Rudder.
Generalities about hooks
Hooks are organized in subdirectories. The root of the sub-directories is /opt/rudder/etc/hooks.d/
Each sub-directory has a name related to the event that will trigger the hooks execution. By default, a hook directory contains a template example and a Readme.txt file explaining the generalities about hooks and the specificities of that hook (parameters, etc).
Hooks must be executable. All executable files will be used as hooks EXCEPT if they end with one of the extensions listed in /opt/rudder/etc/rudder-web.properties for property *rudder.hooks.ignore-suffixes. A common convention is to use the .disabled suffix to do so.
Non executable files will be ignored (which allows to put other files in these directories, like a readme, for example).
Hooks parameter are passed by environment variable. Rudder will fill dedicated environment variable for each hook.
Hooks are executed sequentially, in lexical order. We encourage you to use the patter "NN-hookname", with NN a number like "05", "20", etc.
Hooks have normalized returned code. Return codes on hooks are interpreted as follow:
-
0 : success, no log (apart if debug one) , continue to next hook
-
1-31 : error , error log in /var/log/rudder/webapp/, stop processing
-
32-63 : warning, warning log in /var/log/rudder/webapp/, continue to next hook
-
64-255 : reserved for future use case. Behavior may change without notice.
Hooks have a maximum execution time allowed. After some time (2s for policy generation node specific events, 30s for other cases) a warning will be issued. After a longer time (20s for policy generation node specific events, 5 min for other cases), the hook will be killed. You can change these timeouts with the following directives, that must be in the 1000 first characters of your hook script, prefixed by any type of comments characters (only the end of line is considered):
-
HOOK_WARN_TIMEOUT = <length><unit>
-
HOOK_KILL_TIMEOUT = <length><unit>
Where length is an integer, and unit is one of micro(s), ms, millisecond(s), s,
second(s), m, minute(s), h, hour(s).
Available Hooked events: for now, all hooks are related to different steps of the policy generation process or node lifecycle and inventory reception. In the future, more cases will be supported.
Update campaigns server hooks
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed before and after a campaign event starts to run. This hooks are specific for each campaign, so contrary to other hook layout, for campaign you have: - /opt/rudder/etc/hooks.d/campaigns/ - 781b2837-25d0-4c72-8384-04a22e59d83b // uuid of the campaign - pre-hooks [scripts for pre hooks] - post-hooks [scripts for post hooks]
Hooks return code that stop processing will lead to a "failure" campaign event.
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
CAMPAIGN_ID: the campaign id (ie the name of the json file in /var/rudder/configuration-repository/campaigns)
-
CAMPAIGN_NAME: human readable name of the campaign
-
CAMPAIGN_TYPE: campaign type, ie
system-update,software-update, etc -
CAMPAIGN_EVENT_ID: id of current event triggering that hook
-
CAMPAIGN_EVENT_NAME: human readable name of the event
-
CAMPAIGN_NEXT_STATE: only defined for post-hooks. [failure,finished]. Did we come here because pre-hooks failed?
node-post-acceptance
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed after an inventory was received for an already accepted node and the node information were successfully updated.
Typically, these hooks triggers action on other systems, like updating info on an external CMDB, or send notification.
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_NODE_ID: the nodeId
-
RUDDER_NODE_HOSTNAME: the node fully qualified hostname
-
RUDDER_NODE_POLICY_SERVER_ID: the node policy server id
-
RUDDER_NODE_OS_NAME: OS normalized name (Linux distribution, Windows with version, etc)
-
RUDDER_NODE_OS_VERSION: OS version
-
RUDDER_NODE_OS_SP: OS service pack
-
RUDDER_NODE_OS_STRING: OS long string name
-
RUDDER_NODE_IPS: space separated list of IPs of that node
-
RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE: agent type ("cfengine-community" or "dsc")
node-post-acceptance
node-post-acceptance
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed after an inventory was successfully processed for a node in pending state (never seen, or already pending).
Typically, these hooks triggers action on other system, like registering the node into a monitoring system or into an external CMDB, or to send notification.
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_NODE_ID: the nodeId
-
RUDDER_NODE_HOSTNAME: the node fully qualified hostname
-
RUDDER_NODE_POLICY_SERVER_ID: the node policy server id
-
RUDDER_NODE_OS_NAME: OS normalized name (Linux distribution, Windows with version, etc)
-
RUDDER_NODE_OS_VERSION: OS version
-
RUDDER_NODE_OS_SP: OS service pack
-
RUDDER_NODE_OS_STRING: OS long string name
-
RUDDER_NODE_IPS: space separated list of IPs of that node
-
RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE: agent type ("cfengine-community" or "dsc")
node-post-acceptance
node-post-deletion
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed after a node was successfully deleted.
Typically, these hooks clean resources related to that node and notify external services that the node was deleted from Rudder.
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_NODE_ID: the nodeId
-
RUDDER_NODE_HOSTNAME: the node fully qualified hostname
-
RUDDER_NODE_POLICY_SERVER_ID: the node policy server id
-
RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE : agent type ("cfengine-community" or "dsc")
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_CURRENT: the full path of the base directory containing policies for that node (for ex for nodes under root: /var/rudder/share/$RUDDER_NODE_ID/rules/$RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE)
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_NEW : the full path of the base directory containing next policies for that node (during a generation) (/var/rudder/share/$RUDDER_NODE_ID/rules.new/$RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE)
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_ARCHIVE: the full path of the base directory containing previous policies for that node
-
RUDDER_NODE_KIND: node kind: root, relay or node
node-pre-deletion
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed before a node is deleted.
Typically, these hooks interact with external services using knowledge to validate if the node should actually be deleted.
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_NODE_ID: the nodeId
-
RUDDER_NODE_HOSTNAME: the node fully qualified hostname
-
RUDDER_NODE_POLICY_SERVER_ID: the node policy server id
-
RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE : agent type ("cfengine-community" or "dsc")
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_CURRENT: the full path of the base directory containing policies for that node (for ex for nodes under root: /var/rudder/share/$RUDDER_NODE_ID/rules/$RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE)
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_NEW : the full path of the base directory containing next policies for that node (during a generation) (/var/rudder/share/$RUDDER_NODE_ID/rules.new/$RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE)
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_ARCHIVE: the full path of the base directory containing previous policies for that node
-
RUDDER_NODE_KIND: node kind: root, relay or node
policy-generation-failed
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_GENERATION_DATETIME : ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time that identifies that policy generation.
-
RUDDER_END_GENERATION_DATETIME : ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time when the generation ended (minus these hooks)
-
RUDDER_ERROR_MESSAGE_PATH : path to a file which contains the full error message of the policy generation failure.
policy-generation-finished
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed after policies are fully generated for all nodes, and these new policies are available for download for the node.
Typically, these hooks are used to log information about the generation which just happened or notify third parties that new policies are available (for ex: cf-serverd SIGHUP)
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_GENERATION_DATETIME : ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time that identifies that policy generation.
-
RUDDER_NODE_IDS_PATH : path to a sourceable file with variable RUDDER_NODE_IDS containing a bash array of node id updated during the process, or the empty array if no nodes were updated.
-
RUDDER_END_GENERATION_DATETIME : ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time when the generation ended (minus these hooks)
-
RUDDER_NUMBER_NODES_UPDATED : integer >= 0; number of nodes updated (could be found by counting $RUDDER_NODE_IDS)
-
RUDDER_ROOT_POLICY_SERVER_UPDATED: 0 if root was updated, anything else if not
policy-generation-node-finished
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed after policies are fully generated for node and made available for the node to download.
Typically, these hooks interact with external services using knowledge from the generated policies (ex: send node-properties JSON file to a third party service).
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_GENERATION_DATETIME : generation datetime: ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time that identify that policy generation start
-
RUDDER_NODE_ID : the nodeId
-
RUDDER_NODE_HOSTNAME : the node fully qualified hostname
-
RUDDER_NODE_POLICY_SERVER_ID : the node policy server id
-
RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE : agent type ("cfengine-community" or "dsc")
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_CURRENT: the full path of the base directory containing policies for that node (for ex for nodes under root: /var/rudder/share/$RUDDER_NODE_ID/rules/$RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE)
Technically, you could infer RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_NEW, from RUDDER_NODE_ID, but it’s tedious for nodes behind a relay, and it is just simpler not to have to track what are the Rudder internal names, which may change without notice.
policy-generation-node-ready
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed after policies are fully generated for node, but before these new policies replace the old ones (technically, before we move /var/rudder/share/$NODEID/rules.new to /var/rudder/share/$NODEID/rules).
Typically, these hooks proceed to sanity checks on the new policies (ex: cf-promises), update permission on files, or interact with external services using information from the generated policies (ex: send node-properties JSON file to a third party service).
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_GENERATION_DATETIME : generation datetime: ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time that identify that policy generation start
-
RUDDER_NODE_ID : the nodeId
-
RUDDER_NODE_HOSTNAME : the node fully qualified hostname
-
RUDDER_NODE_POLICY_SERVER_ID : the node policy server id
-
RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE : agent type ("cfengine-community" or "dsc")
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_NEW: the full path of the base directory containing next policies for that node (during a generation) (/var/rudder/share/$RUDDER_NODE_ID/rules.new/$RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE)
Technically, you could infer RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_NEW, from RUDDER_NODE_ID, but it’s tedious for nodes behind a relay, and it is just simpler not to have to track what are the Rudder internal names, which may change without notice.
policy-generation-pre-start
New directives default naming scheme
When a new directive is created, by default the 'Name' field is filled with the Technique name. For example, if you create a new Directive from the 'Users' Technique, the Name field will get the value: "Users".
This not always what you want, especially for your custom Techniques. So you have the possibility to define new default values for Name, at Technique or at Technique and Version granularity.
This is done by adding or updating the file:
/var/rudder/configuration-repository/techniques/default-directive-names.conf.
That file need to be committed in git, and the Technique library reloaded to take effect:
cd /var/rudder/configuration-repository/techniques/ vi default-directive-names.conf .... git add default-directive-names.conf git commit -m "Change default names for new directives" rudder server reload-techniques
The file format is a simple techniqueId[/optionalVersion]: default name to use format.
The Technique ID is the name of the directory containing the Technique version directory
in /var/rudder/configuration-repository/techniques.
For example, if we imagine that in your company, you have the internal convention to create one directive by user role with the login in the name, you would prefer to have a default value to:
Role <user-role>: <matching-login>
And then, for Users Technique version 7, you changed your mind and now use the scheme:
Role: [user-role] (with login [login])
Then the file will look like:
# Default pattern for new directive from "userManagement" technique: userManagement= Role <user-role>: <matching-login> # For userManagement version 2.0, prefer that pattern in new Directives: userManagement/7.0: Role: [user-role] (with login [login])
Policies ordering
Configuration in Rudder is based on desired states, describing the expected state of the system, and not an ordered list of actions to run. However, there are cases where having order is desirable (like ensuring that a JVM is present before deploying an Application server, or ensuring a user is present before setting it sudoers), even if it will converge over the course of several agent runs.
Rudder sorts the policies following this (best-effort) principle:
-
Methods in a technique are executed in the order they appear in the interface
-
Rules are executed in alphanumeric order
-
Inside a rule, directives are executed in alphanumeric order, except for:
-
Mono-instance techniques: only one directive is selected and others are discarded (and they will be tagged as such in node detail compliance)
-
the directive with the highest priority will be selected
-
in case of equal priorities, the rule name and then the directive name are used for sorting them (in alphanumeric order)
-
-
Limited multi-instance techniques: all directives will be merged into one policy on the node
-
the merge order is based on priority, then rule name, and then directive name
-
the place of the merged policy itself in the global policies will be based on the rule and directive names of its most priority source directive
-
-
| The type of a technique is visible when clicking on the technique itself in the directives page. |
|
Best practice
You should always start Rules and Directives name by 2 (or 3) digits to be able to easily reorder Policy evaluation if the need happen: Do not use: "My general security rule" and "Check ssh configuration" But use: "05. My general security rule" and "40. Check ssh configuration" |
Advanced example
-
given three Techniques A, B and C
-
directives A1 and A2 based on Technique A, directives B1 and B2 based on B, directives C1 and C2 based on C
-
all Directives have the same priority,
-
rule R0 having [C1], R1 having [A1, B2] and rule R2 having [A2, B1, C2], all applied on a same node,
-
merging (R0, C1) and (R2, C2) ⇒ [C1, C2] and keep (R0, C1) as Policy order
-
merging (R1, A1) and (R2, A2) ⇒ [A1, A2] and keep (R1, A1) as Policy order,
-
merging (R1, B2) and (R2, B1) ⇒ [B2, B1] (because R1 < R2) and keep (R1, B2) for policy order,
-
so policies are sort: (R0, C1) then (R1, A1) then (R1, B2)
-
resulting ordering of directive’s values will be: [C1, C2] then [A1, A2] then [B1, B2]
Share files between nodes
There is a way to share files from one node to another. It allows a node to send a file to its relay, which will make it available for another target node, that has to specifically download it.
This file sharing method is secured by:
-
The control of uploaded file signature by the server, to check it matches the source node’s private key.
-
The same mechanism as standard file copy in Rudder to download the shared file from the server.
It also includes a ttl mechanism that allows sharing a file for a limited amount of time.
To use this feature, two generic methods are available in the technique editor:
-
sharedfile_from_node: To download a file shared from another node.
-
sharedfile_to_node: To make a file available to another node.
See the documentation of these methods for details about the required parameters, and especially sharedfile_to_node for a complete usage example.
Update technique resources from command line
Techniques can have resource files that are automatically deployed to each node applying these techniques.
Technique resources can be modified via the technique editor interface.
It can however be useful to update a technique resource from outside the interface, for example to update it after an external change.
To do this, on your Rudder server, edit the technique resource file(s) located in
/var/rudder/configuration-repository/techniques/<technique category>/<technique name>/<technique version>/resource
Then add them to git and reload the technique:
cd /var/rudder/configuration-repository/techniques/<technique category>/<technique name>/<technique version>/ git add resource git commit -m"My technique resource updated" rudder server reload-techniques
You’re done.
Import / Export archive of rules, directives, techniques, groups and related dependencies
This feature introduces the possibility to export configuration items (rules, directives, techniques, groups) and
their dependencies (for example, the technique used to define a directive, or the directives and groups for rules) into ZIP archive
and import them back.
This feature may be used to transfer configuration items from a development environment to a qualification one, or to edit by hand in a third party system some aspects of the configuration items and then import them back into Rudder. It is only available through API queries.
This section will present you the main aspect of the feature usage: exports items, control dependency resolution, and import the archive back. For all API related operation, you can check the corresponding API documentation.
Export configuration items
The first aspect of the archive feature allows exporting configuration items and their dependencies into a ZIP archive.
The most common use case is to export a rule and its directives (with related user defined techniques) and groups so that it can be transferred into another
rudder server.
Another common use case is to export a set of configuration items, for example to build a template of a configuration that needs to span on several rules.
Let’s see these two use cases in turn.
The last use case described here will be how to retrieve configuration items at a specific past revision.
Exporting a rule with its directives, techniques and groups
Once you have found the rule’s ID (for example, in the rule details page), you just need to call the export API with that parameter: all dependencies up to techniques are
resolved and included by default. This is equivalent to using the parameter include=all as shown in the command below.
System configuration items are not included in the archive, so for example you will not get system groups used by a rule in the archive (of course, the rule configuration still use them if the archive if imported back).
curl -k -X GET -H "X-API-TOKEN: ...." 'https://rudderhost/rudder/api/latest/archives/export?rules=2278f76f-28d3-4326-8199-99561dd8c785&include=all' -o archive.zip
Archive internal
Now, we will take a quick look at the content of an archive.
Remember, even if the general layout is likely to be stable, file format WILL change.
% unzip archive.zip
Archive: archive.zip
creating: archive/
....
% ls
archive archive.zip
% tree archive
.
├── directives
│ ├── 10_-_default_time_setting.json
│ └── 20_-_Welcome_message.json
├── groups
│ ├── Agents.json
│ ├── All_centos.json
│ └── All_debian.json
├── rules
│ └── Generic_rule_for_all_env.json
└── techniques
└── systemSettings
├── misc
│ └── clockConfiguration
│ └── 3.1
│ ├── changelog
│ ├── clockConfiguration.st
│ ├── metadata.xml
│ └── tz_vars.st
└── systemManagement
└── motdConfiguration
└── 3.3
├── changelog
├── config.st
├── main.st
├── metadata.xml
└── motd.ps1.st
We see that the archive has a standard directory layout looking like the one in /var/rudder/configuration-repository.
In each directory, you find serialisation of the corresponding configuration items.
For rules, directives, and groups, the file has the item name normalized. The content is the same as the one you get when you query the item details on REST API.
For techniques, the subdirectory layout and technique content is exactly the same as the one in have in /var/rudder/configuration-repository/techniques.
You can update content in that archive, create a new ZIP with the following command, and import it back into rudder to update policies.
For example:
-
edit the rule
shortDescriptionproperty inarchive/rules/Generic_rule_for_all_env.json -
zip back:
% zip -r archive.zip archive adding: archive/ (stored 0%) adding: archive/techniques/ (stored 0%) adding: archive/techniques/systemSettings/ (stored 0%) ...
And see next chapter for importing it.
Exporting a set of rules and directives for configuration templating
Another common use case is when you need several rules with specific directive to achieve a configuration need on several OS - typically, you want to enforce
some security checks on Debian and Redhat, but these checks vary.
So you develop things in QA, and when it’s ok, you import them prod - but not the groups, which are different.
For that, you will restrict the scope of what dependencies are included in the archive (rule1 and rule2 are used in place of UUIDs for readability):
curl -k -X GET -H "X-API-TOKEN: ...." 'https://rudderhost/rudder/api/latest/archives/export?rules=rule1,rule2&include=directives,techniques' -o archive.zip
And if you still need a specific group, directive or technique, or directive added in the archive, just add them in the query:
curl -k -X GET -H "X-API-TOKEN: ...." 'https://rudderhost/rudder/api/latest/archives/export?rules=...&directives=...&groups=...&techniques=...&include=directives,techniques' -o archive.zip
Extracting configuration items from a past revision
Finally, you can obtain an archive with configuration from a past revision. Just append the revision to the item id after a URL-encoded + (ie %2B) and its dependencies will be resolved for the same revision.
For example, for getting a rule and its dependencies from revision with commit ID 5962a856684ab8ce2363f302ed4ee9455786fd03, use the command:
curl -k -X GET -H "X-API-TOKEN: ...." 'https://rudderhost/rudder/api/latest/archives/export?rules=2278f76f-28d3-4326-8199-99561dd8c785%2B5962a856684ab8ce2363f302ed4ee9455786fd03' -o archive.zip
Import configuration items
Import feature is very unsophisticated in that version. In particular, you need to know: - that the archive format is expected to be the one from the export feature, bad serialization format will lead to errors, - that configuration items with the same UUID as in the archive will be overwritten.
Once you’re ready, importing an archive is done with that REST API call:
curl -k -X POST -H "X-API-TOKEN: ...." https://rudderhost/rudder/api/latest/archives/import --form "archive=@archive.zip"
Where archive.zip is the path toward your archive file.
Log information relative to archives processing server-side
Archives import/export feature has its own logger named application.archive.
You can get more information about what is happening in /var/log/rudder/webapp/webapp.log by adding the following logger definition in file
/opt/rudder/etc/logback.xml (no need to restart rudder after change) above lines YOU SHOULD NOT HAVE TO CHANGE THINGS BELOW THAT LINE:
<logger name="application.archive" level="debug" />
← Variables REST API →