Advanced node management
Reinitialize policies for a Node
To reinitialize the policies for a Node, delete the local copy of the applied policies fetched from the Rudder Server, and create a new local copy of the initial policies.
rudder agent reset
At next run of the Rudder Agent (it runs every five minutes), the initial policies will be used.
|
Use this procedure with caution: the applied policies of a Node should never get broken, unless some major change has occurred on the Rudder infrastructure, like a full reinstallation of the Rudder Server. |
Completely reinitialize a Node
You may want to completely reinitialize a Node to make it seen as a new node on the server, for example after cloning a VM.
|
This command will permanently delete your node uuid and keys, and no configuration will be applied before re-accepting and configuring the node on the server. |
The command to reinitialize a Node is:
rudder agent factory-reset
This command will delete all local agent data, including its uuid and keys, and
also reset the agent internal state. The only configuration kept is the server
hostname or ip configured in policy_server.dat. It will also send an inventory
to the server, which will treat it as a new node inventory.
Change the agent run schedule
By default, the agent runs on all nodes every 5 minutes. You can modify this value in Settings → General page in Agent Run Schedule section, as well as the "splay time" across nodes (a random delay that alters scheduled run time, intended to spread load across nodes).

This settings can also be modified Node by Node, allowing you to customize the agent behavior (Node with little resource like a Raspberry Pi or with limited bandwidth). To do that, go into the Node details in the Settings tab
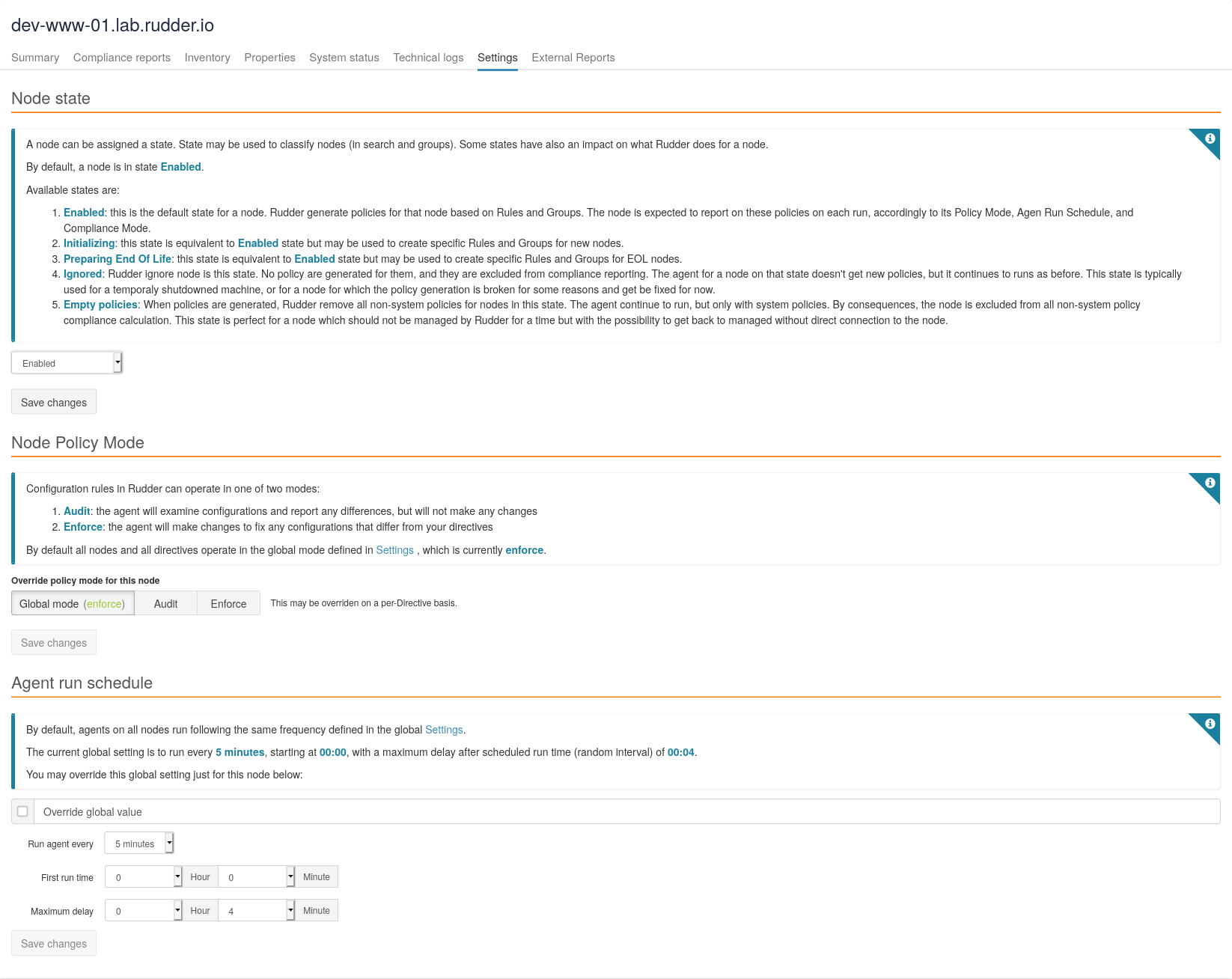
|
When reducing notably the run interval length, reporting can be in 'No report' state until the next run of the agent, which can take up to the previous (longer) interval. |
Installation of the Rudder Agent
Static files
At installation of the Rudder Agent, files and directories are created in following places:
- /etc
-
Scripts to integrate Rudder Agent in the system (init, cron).
- /opt/rudder/share/bootstrap-promises
-
Bootstraping policies for the Rudder Agent. These policies are used to download a common set of initial policies from the server.
- /opt/rudder/lib/perl5
-
The FusionInventory Inventory tool and its Perl dependencies.
- /opt/rudder/bin/run-inventory
-
Wrapper script to launch the inventory.
- /opt/rudder/bin
-
Binaries for agent.
- /var/rudder/cfengine-community
-
This is the working directory for the agent.
Generated files
At the end of installation, the agent’s working directory is populated for first use, and unique identifiers for the Node are generated.
- /var/rudder/cfengine-community/bin/
-
agent binaries are copied there.
- /var/rudder/cfengine-community/inputs
-
Contains the actual working policies. Initial policies are copied here at installation. After validation of the Node, Applied Policies, which are the policies generated by Rudder for this particular Node, will be stored here.
- /var/rudder/cfengine-community/ppkeys
-
An unique SSL key generated for the Node at installation time.
- /opt/rudder/etc/uuid.hive
-
An unique identifier for the Node is generated into this file.
Services
After all of these files are in place, the agent daemons are launched:
Unresolved include directive in modules/usage/pages/advanced_node_management.adoc - include::partial$/glossary/cf-execd.adoc[]
Unresolved include directive in modules/usage/pages/advanced_node_management.adoc - include::partial$/glossary/cf-serverd.adoc[]
Rudder Agent interactive
You can force the Rudder Agent to run from the console and observe what happens.
rudder agent run
|
Error: the name of the Rudder Root Server can’t be resolved
If the Rudder Root Server name is not resolvable, the Rudder Agent will issue this error: rudder agent run Unable to lookup hostname (rudder-root) or cfengine service: Name or service not known To fix it, either you set up the agent to use the IP address of the Rudder root server instead of its Domain name, either you set up accurately the name resolution of your Rudder Root Server, in your DNS server or in the hosts file. The Rudder Root Server name is defined in this file echo *IP_of_root_server* > /var/rudder/cfengine-community/policy_server.dat |
|
Error: the rudder-agent service is not responding on the Rudder Root Server
If the rudder-agent is stopped on the Rudder Root Server you will get this error: # rudder agent run !! Error connecting to server (timeout) !!! System error for connect: "Operation now in progress" !! No server is responding on this port Unable to establish connection with rudder-root Restart the rudder-agent service: service rudder-agent restart |
Processing new inventories on the server
Verify the inventory has been received by the Rudder Root Server
There is some delay between the time when the first inventory of the Node is sent, and the time when the Node appears in the New Nodes of the web interface. For the brave and impatient, you can check if the inventory was sent by listing incoming Nodes on the server:
ls /var/rudder/inventories/incoming/
Process incoming inventories
On the next run of the agent on Rudder Root Server, the new inventory will be detected and sent to the Inventory Endpoint. The inventory will be then moved in the directory of received inventories. The Inventory Endpoint do its job and the new Node appears in the interface.
You can force the execution of agent on the console:
rudder agent run
Prepare policies for the Node
Policies are not shared between the Nodes for obvious security and confidentiality reasons. Each Node has its own set of policies. Policies are generated for Nodes according in the following cases;
-
A new node was accepted;
-
Inventory has changed;
-
Technique has changed;
-
Directive has changed;
-
Group of Node has changed;
-
Rule has changed;
-
Regeneration was forced by the user.
Agent execution frequency on nodes
Checking configuration
By default, Rudder is configured to check and repair configurations using the agent every 5 minutes, at 5 minutes past the hour, 10 minutes past the hour, etc.
The exact run time on each machine will be delayed by a random interval, in order to "smooth" the load across your infrastructure (also known as "splay time"). This reduces simultaneous connections on relay and root servers (both for the policy server and for sending reports).
See the agent run schedule section to see how to configure it
Inventory
The FusionInventory agent collects data about the node it’s running on such as machine type, OS details, hardware, software, networks, running virtual machines, running processes, environment variables…
This inventory is scheduled once every 24 hours, and will happen in between 0:00 and 5:00 AM. The exact time is randomized across nodes to "smooth" the load across your infrastructure.
Extend node inventory
It is quite common to need to gather information on your nodes that are not present in the standard Rudder inventory information.
As of Rudder 4.3.0, you can get more information about a node thanks to
inventory hooks. These information will be available as standard node properties.
Starting from 6.0.3, the inventory extension is also available on DSC based agents.
Overview
On the node, you create inventory hooks executable and place them in /var/rudder/hooks.d.
These binaries are executed in the alphanumerical order, only if executable, and their output is checked to
ensure that it is proper JSON.
On DSC based agents, they must be powershell scripts and be located under C:\Program Files\Rudder\hooks.d.
For example, one hook can output:
{
"my_prop1": ["a", "json", "array"],
"my_prop2": {"some": "more", "key": "value"}
}
When the node inventory is processed server side, the node properties will get new values, one per first-level key of all hooks.
These node properties are marked as "provided by inventory" and can not be deleted nor overwritten. Apart from that characteristic, they are normal node properties that can be used to create group, or as variables in Directives parameters.
Creating a node inventory hook
An inventory hook can be any kind of executable that can be called without parameters, from a shell script to a C program.
Hooks are located in directory /var/rudder/hooks.d. You may need to create that directory the first time you want to add hooks:
mkdir /var/rudder/hooks.d
They need to be executable by rudder agent.
For example, this hook will create a new "hello_inventory" node property:
% cd /var/rudder/hooks.d
% cat <<EOF > hello-world
#!/bin/sh
echo '{"hello_inventory": "a simple string value from inventory"}'
EOF
% chmod +x hello-world
% rudder agent inventory
And then, after the server has processed the inventory, the node (here with ID '74d10806-b41d-4575-ab86-8becb419949b') has the corresponding property:
% curl -k -H "X-API-Token: ......" -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X GET 'https://..../rudder/api/latest/nodes/74d10806-b41d-4575-ab86-8becb419949b?include=minimal,properties' | jq '.'
{
"action": "nodeDetails",
"id": "74d10806-b41d-4575-ab86-8becb419949b",
"result": "success",
"data": {
"nodes": [
{
"id": "74d10806-b41d-4575-ab86-8becb419949b",
....
"properties": [
{
"name": "hello_inventory",
"value": "a simple string value from inventory",
"provider": "inventory"
}
]
}
]
}
}
Node Lifecycle
Imagine you have a node that you must disconnect for a maintenance period.
You know what is happening on the node, and during the maintenance period,
you don’t want that the Rudder shows up the node as Not responding
and trigger alert on global compliance level.
An other common use case is to be able to set specific policies for nodes just after acceptation that are used for provisioning, or just before node end of life to clean it up.
In Rudder 4.3, we introduced a way to manage the Node lifecycle, for both of theses uses cases:
-
nodes disconnected from Rudder Server can be excluded from policy generation and Compliance with the
Ignoredstate, -
the main states of a system life can be applied with the 4 states
Initializing,Enabled,Preparing End of LifeandEmpty policies.
States Ignored and Empty policies automatically changes the policy generation and compliance:
-
Ignoredprevents any new policy generation for the Nodes in this states. -
Empty policiesgenerates a minimal set of policies, only to manage the Rudder Agent itself.
Both states remove the nodes from the compliance.
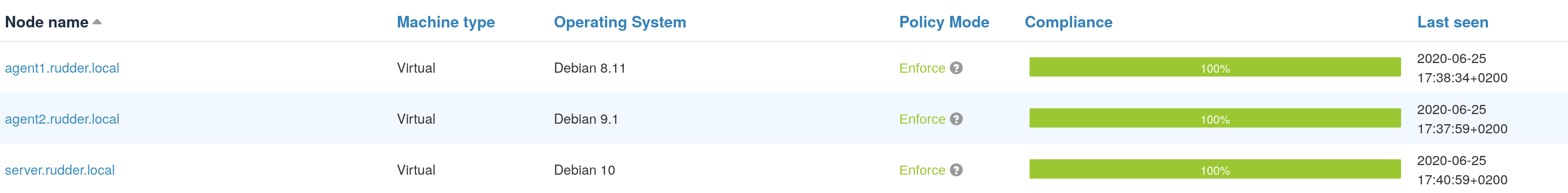
Nodes with non-default state appears with a label next to their name in the nodes list to show their
states, and their compliance doesn’t show up in Ignored nor Empty policies mode. You can filter by
node lifecycle state in that list with the common Filter input field.
Node with a given lifecycle state can be searched thanks to the quick search tool in Rudder status
bar. That state can also be used to construct groups (Node state attribute of Node summary)
and they also show up in the API responses concerning node information.
Finally, the default state for a Node can be configured in the Settings page, to define in which mode accepted Nodes use.

In the future, these states will be configurable on a per node basis at acceptation, and the lifecycle states list will be configurable by users.
Disable the service listening for remote run on nodes
By default, every Rudder node runs a service that listens on port 5309 for remote execution triggers, callable from Rudder API.
| On Rudder root server and relays, this service is necessary and cannot be disabled. It is used to serve configuration policies to managed nodes. |
It is totally optional, and you can easily disable it:
-
On systemd systems, stop and disable the
rudder-cf-serverdservice on the nodes you don’t want it to run (you can do it through Rudder policies):
systemctl stop rudder-cf-serverd.service systemctl disable rudder-cf-serverd.service
-
On systems still using the init script, edit
/etc/default/rudder-agentand uncomment and set to 0 theCFENGINE_COMMUNITY_RUN_1line:
CFENGINE_COMMUNITY_RUN_1="0"
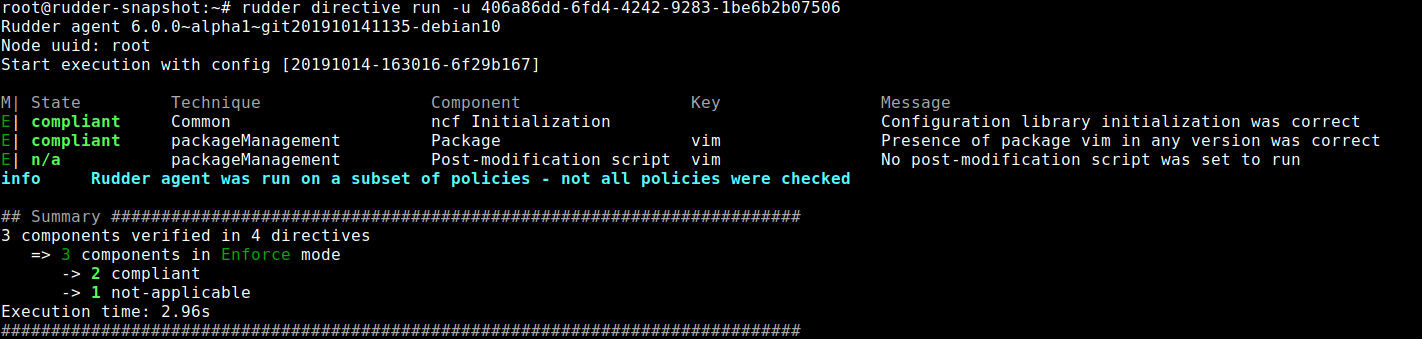
Single directive execution
Normal rudder agent runs apply all the node configuration to the underlying system.
You may sometimes want to test a single directive, either because it is long to run or because you want to test it in isolation from directives.
To do this, you need to know the list of available directives on your agent with the command:
rudder directive list
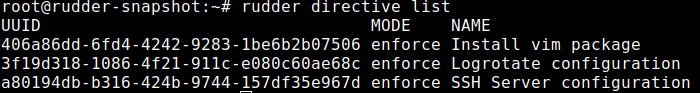
Then you can run one with the command:
rudder directive run -u <uuid>
← Node management Configuration concepts →