Advanced configuration management
Policy generation
Each time a change occurs in the Rudder interface, having an impact on the policy needed by a node, it is necessary to regenerate the modified policies for every impacted node. By default this process is launched after each change.
The process of policy generation:
-
Use configured policies and information about the nodes to generate the files defining the policy that reflects the desired state
-
Compute and store expected reports that will be produced when executing these policies
-
Check the validity of the generated policies
-
Replace the old version of the policies by the new one for impacted node
-
Restart the policy server on the Rudder central server is authorizations have changed
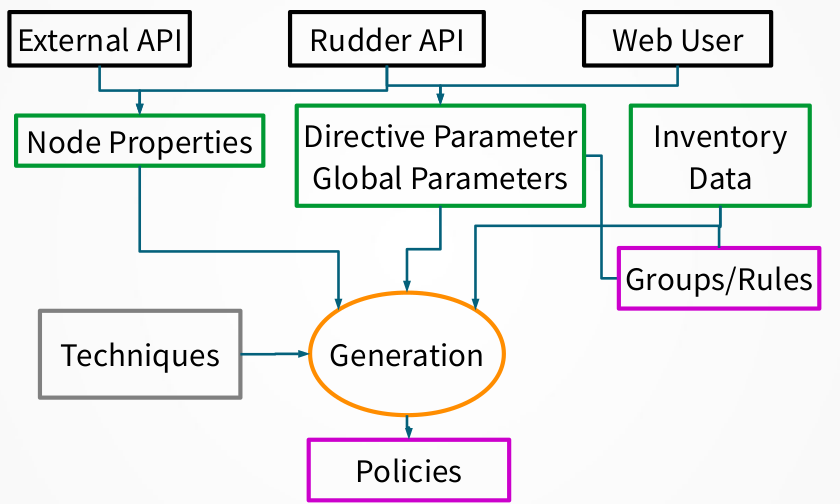
You can customize some of these actions and add new ones using the Server Event Hooks.
Update policies button
The button Update policies on the top right of the screen, in the Status menu, allows you to force the regeneration of the policies. As changes in the inventory of the nodes are not automatically taken into account by Rudder, this feature can be useful after some changes impacting the inventory information.
Regenerate all policies button
The button Regenerate all policies on the top right of the screen, in the Status menu, allows you to force the regeneration of all policies. It will clear all internal caches, and force a complete computation of the policies. This is generally useful to make sure everything is correct after a problem on the central server.
Policy generation info log
Policy generation is a complex process and it is central to Rudder use. You will often want to know more about a policy generation result: what was the reason for a failure? What nodes where upated? Or even more specifics info like: where are info and debug log?
/var/rudder/policy-generation-info
Directory /var/rudder/policy-generation-info contains information about the last policy generation(s)
in the following files:
-
last-failure-message: when a generation fails, failure message is stored here. It is helpful for debugging purpose (for example when message is very long), or to know what happened in case of transient errors. -
last-updated-nodeids: this file contains list of node updated in last generation. It is in a source-able format which defined three bash array: -
RUDDER_UPDATED_POLICY_SERVER_IDS: contains the set of updated policy servers (root or relay) -
RUDDER_UPDATED_NODE_IDS: contains the set of updated standard nodes -
RUDDER_NODE_IDS: contains both updated policy server and nodes. Policy servers always come first.
Each file starts with a comment describing what policy generation generated it.
Two version of each of these files is concerved: the oldest one has a .old suffix.
webapp logs
Rudder web application logs located in /var/log/rudder/webapp/yyyy_MM_dd.stderrout.log contains information
about policy generation process. In rudder 6.0, all policy generation logs are gathered under policy.generation
namespace (with optionally more precise namespace, like policy.generation.timing for timing information, or
policy.generation.update for updated nodes, etc).
By default, policy generation logs when it starts with generic information about system:
[2020-03-12 15:32:28+0100] INFO policy.generation - Start policy generation, checking updated rules [2020-03-12 15:32:29+0100] INFO policy.generation - [metrics] Xmx:1.55 GB nodes:8 (cached:0) rules:248 (enabled:35) techniques:131 (enabled:127) directives:238 (enabled:224) groups:26 (dynamic:17) parameters:3
How many nodes were updated:
[2020-03-12 15:32:39+0100] INFO policy.generation - Configuration of 8 nodes were updated, their policies are going to be written
Timing information about generation steps (they are always logged to allows to check general performance evolution):
[2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Timing summary: [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Run pre-gen scripts hooks : 200 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Run pre-gen modules hooks : 19 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Fetch all information : 325 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Historize names : 7004 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Build current rule values : 327 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Build target configuration : 2277 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Write node configurations : 57132 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Save expected reports : 80 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Run post generation hooks : 411 ms [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Number of nodes updated : 8 [2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation.timing - Policy generation succeeded in: 1 min 9 s
End finally summary of generation: success or failure, total time:
[2020-03-12 15:33:37+0100] INFO policy.generation - Successful policy update '10198' [started 2020-03-12 15:32:28 - ended 2020-03-12 15:33:37]
Much more information can be logged about policy generation (hook execution and timing, much more precise timing,
updated nodes, files writen, etc). All corresponding logs and verbosity levels are documented and controlled
in /opt/rudder/etc/logback.xml.
Understanding how Technique Editor works
In this chapter, we are giving an overview about how the Technique Editor works and how it is integrated with the main Rudder application.
Directory layout
As explained in http://www.ncf.io/, ncf uses a structured directory tree composed of several layers of logic, from internal libraries to Techniques and user services. All the files and logic in these folders will be named "library" for simplicity
ncf directory structure exists in two root folders:
-
/usr/share/ncf/tree-
This is the standard library installation folder. It is created and updated by the the ncf package. This folder will be completely overwritten when you update ncf package so you should never modify anything here: it will be lost at some point.
-
-
/var/rudder/configuration-repository/ncf-
This is were you add your own ncf Generic Methods and Techniques. Techniques created with the Technique Editor will be located here, and both Generic and Techniques in that place will be accessible in the Technique Editor alongside what is provided by the standard library.
-
Sharing ncf code with nodes
To share those folders to all nodes, Rudder makes a copy of these folders in two places:
-
/var/rudder/ncf, for part common to all nodes - so NOT techniques,-
/var/rudder/ncf/localis a copy of node-independent directories from/var/rudder/configuration-repository/ncf, so almost everything BUT/var/rudder/configuration-repository/ncf/50_techniques. -
/var/rudder/ncf/commonis a copy/usr/share/ncf/tree
-
-
/var/rudder/share/xxxx-yyyy-node-id-zzzz/rules/cfengine-community/Technique_Name/1.0/Technique_Name.cffor techniques, with one directory for each technique applied to the node. -
/var/rudder/share/xxxx-yyyy-node-id-zzzz/rules/cfengine-community/rudder_expected_reports.csvcontains information about report expected for all ncf techniques applied to that node.
Files in /var/rudder/ncf are synchronized automatically by the "rudder agent update"
command when the agent runs on the server. So any modification done in files
in these directories will be lost at the next synchronization.
Files under /var/rudder/share/ are updated during policy generation.
A node updates its ncf local library by copying the content of these two folders during its policy update phase.
From ncf Technique Editor to Rudder Techniques and back
Here we will explain how the Technique Editor integration to Rudder is done to transform ncf techniques into full fledged Rudder one. We will also get the big picture of the web flow and the resulting events triggered on Rudder server side.
Each action in the Technique Editor interface produces requests to an API defined over ncf.
All of the requests are authenticated thanks to a token passed in the JSESSIONID header. The token is generated when an authenticated user is connected to the Rudder interface (typically thanks to his browser).
That token is shared to the Technique Editor interface, which itself passes the JSESSIONID header to all requests.
If you have authentication issue, check that your Rudder session is not expired.
- Get request
-
Get request will get all Techniques and Generic Methods in a path passed as parameters of the request in the "path" javascript variable:
Get requests are triggered when accessing Technique editor.
The ncf API will parse all files in the parameter path by running "cf-promises -pjson" on all Techniques, checking that all Techniques are correctly formed.
The ncf API will also look to all Generic Methods description data to build the catalog of available Generic Methods.
The resulting information are sent back to the Technique Editor for displaying.
- Post requests
-
Post requests are issued when a Technique is created, modified or deleted. They will only work on Techniques available in the path given in parameter.
They are triggered when clicking on save/delete button.
The main difference with get requests is that hooks are launched before and after the action is made.
We will see all hooks behavior in the following dedicated hooks section.
Hooks
On each POST request, pre- and post- hooks are executed by the Technique Editor. These hooks are used for the Rudder integration to help transform pure ncf Techniques into Rudder one.
-
pre-hooks are located in:
/var/rudder/configuration-repository/ncf/pre-hooks.d -
post-hooks are located in:
/var/rudder/configuration-repository/ncf/post-hooks.d
As of March 2015, we have two post-hooks defined and no pre-hooks:
-
post.write_technique.commit.sh-
It commits the Technique newly created into Rudder Git configuration repository located in
/var/rudder/configuration-repository.
-
-
post.write_technique.rudderify.sh-
It generates a valid Rudder Technique from a the newly created Technique and reloads Rudder Technique Library so that updates are taken into account.
-
If you want to run post hooks by hand, you can use the following command:
/var/rudder/configuration-repository/ncf/post-hooks.d/post.write_technique.commit.sh /var/rudder/configuration-repository bundle_name
Node properties
Node properties can be found in the properties tab of each node in Rudder.
Node properties can be modified using Rudder’s API, see https://docs.rudder.io/api/#api-Nodes-updateNodeProperties
Properties can also be defined on the node itself, to override locally properties.
Each property is a key=value pair. The value can be a string or a well-formatted JSON data structure.
Some examples:
datacenter=Paris
datacenter= { "id": "FRA1", "name": "Colo 1, Paris", "location": "Paris, France", "dns_suffix": "paris.example.com" }
Using properties
You can use node properties almost everywhere in Rudder:
-
in directive parameters
-
in the technique editor
-
in your own techniques and generic methods
To use a property, simply use the variable node.properties with the variable call syntax.
Example with a property named 'datacenter':
${node.properties[datacenter]}
In a mustache template, use:
{{{vars.node.properties.datacenter}}}
Local override
The agent searches for optionnal properties files /var/rudder/local/properties.d/*.json, and will override existing properties.
As a result, if you have node properties defined server side as
"sysctls_postgresql":{"kernel.shmall":"903330","kernel.shmmax":"3700041320"} and
"vm":{"vm.dirty_ratio":"10"}
and a local property file /var/rudder/local/properties.d/postgresql_config.json as
{
"properties":
{
"sysctls_postgresql": {
"kernel.shmmax":"5368709120"
}
}
}
The resulting properties will be:
"sysctls_postgresql":{"kernel.shmmax":"5368709120"} and
"vm":{"vm.dirty_ratio":"10"}
sysctls_postgresql has been overriden by local property, and vm has been left untouched.
Note that it is an override, as the semantic of merging is not deterministic with literal values, and it does not allow to unset values. If you need to merge, please refer to the next paragraph.
Merging properties
If you want to merge server defined properties with local defined properties, rather than override them, you will need to use the generic method variable_dict_merge_tolerant to define which variables you need to merge, and define the local variables in a different namespace than properties.
For instance, if you have defined in the node properties the following properties
"sysctls_postgresql":{"kernel.shmall":"903330","kernel.shmmax":"3700041320"}
and you wish to merge these values on a node with locally defined variable, to change the value of kernel.shmmax and set the value of kernel.shmmni, you can define the file /var/rudder/local/properties.d/postgresql_config.json with the following content
{
"local_properties":
{
"sysctls_postgresql": {
"kernel.shmmax":"5368709120",
"kernel.shmmni":"4096"
}
}
}
and use the generic method variable_dict_merge_tolerant to merge node.properties[sysctls_postgresql] and node.local_properties[sysctls_postgresql], and set the result in merged_properties.sysctls_postgresql (for instance): variable_dict_merge_tolerant("merged_properties", "sysctls_postgresql", "node.properties[sysctls_postgresql]", "node.local_properties[sysctls_postgresql]")
As a result, merged_properties.sysctls_postgresql will contain
"sysctls_postgresql": { "kernel.shmall":"903330", "kernel.shmmax":"5368709120", "kernel.shmmni":"4096" }
Under the hood
On the server, one or more properties files are written for each node in the
/var/rudder/share/<uuid>/rules/cfengine-community/properties.d/ directory.
This directory is then copied to each node by the agent with all other policy files.
In the agent, properties are made available in the node.<namespace> container that contains the values.
Those values are read from
/var/rudder/cfengine-community/inputs/properties/*.json. All files are taken
in order and override the previous ones - the last one wins.
The agent searches for optional properties files /var/rudder/local/properties.d/*.json, and will define variables
or override existing properties.
Each file must contain at least 2 levels of JSON content, the first level is the namespace level and the second level is the key level.
The namespace name must be an ASCII name that doesn’t start with and must
match the following regex: [a-zA-Z0-9][a-zA-Z0-9]*
For example:
{
"properties":
{
"datacenter": "Paris",
"environment": "production",
"customer": "Normation"
}
}
The merge is a first level merge done at the namespace level. This means that:
-
a key in a namespace is fully overridden by the same key in the same namespace in a later file.
-
a key in a namespace is never overridden by the same key in a different namespace
-
a key that is overridden never retains original data even if it is a data container itself
The result key is available in the node.<namespace> data variable. A usage
example:
${node.properties[datacenter]}
To get the original data (for debug only) there is the
properties.property_<fileid> variable. A usage example:
${properties.property__var_rudder_cfengine_community_inputs_properties_d_properties_json[properties][datacenter]}
Node properties expansion in directives
It is possible to use properties defined on nodes to build Directive values in all fields. The resulting values will be computed during policy generation, and can therefore provide unique values for each node or be used in JavaScript expressions.
Properties on nodes are defined using Rudder’s REST API, with the 'Update Node properties' API call. More details in our API documentation.
Properties can also be defined directly on the nodes, by creating properties files
/var/rudder/local/properties.d/*.json/
Feature availability
If you upgraded to 3.1.14 (or a later 3.1.x version) or 3.2.7 (or a later 3.2.x version) from a previous Rudder version, this feature was disabled by default in order to mitigate any risk of undesired side effects on existing installations. You can enable it in the Administration/Settings page, using the Enable node properties expansion in Directives switch.
Rudder installations from 4.0.0 onwards have this feature enabled by default.
Usage
In any directive text field, you can access properties defined on nodes using the following syntax:
${node.properties[property_name][key_one][key_two]}
where:
-
property_nameis the name of the property defined via the API -
key_oneandkey_twoare keys in the JSON structure -
the value obtained is the string representation, in compact mode, of the entire node property or sub-structure of the JSON value
-
if the key is not found, an error will be raised that will stop policy generation
-
spaces are authorized around separators ([,],|,}..)
Providing a default value
Most of the time, you will need to provide a default value to node properties expansion to avoid a policy generation error due to missing node properties. This is also a good case to allow a simple override mechanism for a parameter where only some nodes have a specific value.
You can also use other node properties, or other Rudder parameters as defaults, using the same syntax as above.
Some examples:
${node.properties[datacenter][id] | default = "LON2" }
${node.properties[datacenter][name] | default = """Co-location with "Hosting Company" in Paris (allows quotes)""" }
${node.properties[datacenter][id] | default = ${rudder.param.default_datacenter} }
${node.properties[netbios_name] | default = ${rudder.node.hostname} }
${node.properties[dns_suffix] | default = ${node.properties[datacenter][dns_suffix] | default = "${rudder.node.hostname}.example.com" }
#or even use cfengine variables in the default
${node.properties[my_override] | default = "${cfengine.key}"}
Forcing expansion on the node
In some cases, you will want to use a ${node.properties[key]} in a directive parameter, but you don’t want to expand it during
policy generation on the Rudder server, but instead let the value be expanded during the agent run on the node. Typically if the value is to be used by a templating
tool, or if the value is known only on the node.
For these cases, you can add the "node" option to the property expression:
${node.properties[datacenter][id] | node }
This will be rewritten during policy generation into:
${node.properties[datacenter][id]}
Which will be considered as a standard variable by the agent, which will replaced this expression by its value if it’s defined, or kept as is if it’s unknown.
The variable content is read from /var/rudder/cfengine-community/inputs/properties.d/properties.json, and from the optionally defined /var/rudder/local/properties.d/*.json files.
You can find more information on node properties in node properties documentation.
JavaScript evaluation in Directives
It is possible to use JavaScript expressions to build Directive values. The resulting values will be computed during policy generation, and can therefore provide unique values for each node.
Feature availability
If you upgraded from a version prior to 3.1.12 or 3.2.5, this feature is disabled by default in order to mitigate any risk of undesired side effects on existing installations. You can enable it in the Administration/Settings page, using the Enable script evaluation in Directives parameter.
Rudder installations from 4.0 onwards have this feature enabled by default.
Usage
All standard JavaScript methods are available, and a Rudder-specific
library, prefixed with rudder. also provides some extra utilities. This
library is documented below.
For example, to get the first 3 letters of each node’s hostname, you can write:
"${rudder.node.hostname}".substring(0,3)
|
Limitation of the scripting language
JavaScript expressions are evaluated in a sandboxed JavaScript environment. It has some limitations, such as:
|
Rudder utility library
Standard hash methods
The following methods allow to simply hash a value using standard algorithms:
-
rudder.hash.md5(string) -
rudder.hash.sha256(string) -
rudder.hash.sha512(string)
These methods do not use a salt for hashing, and as such are not suitable for distributing passwords for user accounts on UNIX systems. See below for a preferable approach for this.
UNIX password-compatible hash methods
The following methods are specially designed to provided hashes that can be
used as user passwords on UNIX systems (in /etc/shadow, for example). Use
these if you want to distribute hashes of unique passwords for each of your
nodes, for example.
Two different cases exist: support for generic Unix-like systems (Linux, BSD, …) and support for AIX systems (which use a different hash algorithm).
Available methods are:
-
rudder.password.auto(algorithm, password [, salt]) -
rudder.password.unix(algorithm, password [, salt]) -
rudder.password.aix(algorithm, password [, salt])
The parameters are:
-
algorithmcan be "MD5", "SHA-512", "SHA512", "SHA-256", "SHA256" (case insensitive) -
passwordis the plain text password to hash -
saltis the optional salt to use in the password (we strongly recommend providing this value - see warning below)
The unix method generates Unix crypt password compatible hashes (for use on
Linux, BSD, etc), while the aix method generates AIX password compatible
hashes. The auto method automatically uses the appropriate algorithm for
each node type (AIX nodes will have a AIX compatible hash, others will
have a Unix compatible hash). We recommend always using auto for simplicity.
For example, to use the first 8 letters of each node’s hostname as a password, you could write:
rudder.password.auto("SHA-256", "${rudder.node.hostname}".substring(0,8), "abcdefg")
|
Providing a salt
It is strongly recommended to provide a salt to the methods above. If no salt is provided, a random salt is created, and will be recreated at each policy generation, causing the resulting hashes to change each time. This, in turn, will generate an unnecessary "repaired" status for the password component on all nodes at each policy generation. |
|
JVM requirements
This features is tested only on HotSpot 1.7 and 1.8, OpenJDK 1.7 and 1.8, IBM JVM 1.7 and 1.8. |
|
JVM requirements for AIX password hashes
AIX password generation depends on the availability of PBKDF2WithHmacSHA256 and PBKDF2WithHmacSHA512 in the JVM. These algorithms are included by default on HotSpot 1.8 and OpenJDK 1.8 and upward. In the case where your JVM does not support these algorithms, typically on an IBM JDK or a JVM 1.7 version of HotSpot and OpenJDK, the hashing algorithm falls back to SHA1 with PBKDF2WithHmacSHA1, and an error message will be logged. You can also check your JVM editor manual to add support for these algorithms. |
Status and future support
In a future version of Rudder, JavaScript evaluation will be supported in all fields in Directives, including non plain-text fields.
In the meantime, you can already test this functionality out by entering a JavaScript
expression in any Directive field, prefixed by evaljs:. Please be aware that
this is unsupported and untested, so do this at your own risk.
If you do encounter any issues, please get in touch or open a ticket - we’d love to hear about them!
There is currently no plan to extend this support to the fields in the Technique editor.
Server Event Hooks
Rudder 4.1 introduces the possibility to execute files (hooks), typically scripts, when some predefined event occurs on Rudder.
Generalities about hooks
Hooks are organized in subdirectories. The root of the sub-directories is /opt/rudder/etc/hooks.d/
Each sub-directory has a name related to the event that will trigger the hooks execution. By default, a hook directory contains a template example and a Readme.txt file explaining the generalities about hooks and the specificities of that hook (parameters, etc).
Hooks must be executable. All executable files will be used as hooks EXCEPT if they end with one of the extensions listed in /opt/rudder/etc/rudder-web.properties for property *rudder.hooks.ignore-suffixes. A common convention is to use the .disabled suffixe to do so.
Non executable files will be ignored (which allows to put other files in these directories, like a readme, for example).
Hooks parameter are passed by environment variable. Rudder will fill dedicated environment variable for each hooks.
Hooks are executed sequentially, in lexical order. We encourage you to use the patter "NN-hookname", with NN a number like "05", "20", etc.
Hooks have normalized returned code. Return codes on hooks are interpreted as follow:
-
0 : success, no log (appart if debug one) , continue to next hook
-
1-31 : error , error log in /var/log/rudder/webapp/, stop processing
-
32-63 : warning, warning log in /var/log/rudder/webapp/, continue to next hook
-
64-255 : reserved for future use case. Behavior may change without notice.
Available Hooked events: for now, all hooks are related to different steps of the policy generation process. In the future, more hooks will be supported like node acceptation.
node-post-acceptance
node-post-deletion
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed after a node was successfully deleted.
Typically, these hooks clean resources related to that node and notify external services that the node was deleted from Rudder.
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_NODE_ID: the nodeId
-
RUDDER_NODE_HOSTNAME: the node fully qualified hostname
-
RUDDER_NODE_POLICY_SERVER_ID: the node policy server id
-
RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE : agent type ("cfengine-nova" or "cfengine-community")
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_CURRENT: the full path of the base directory containing policies for that node
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_NEW: the full path of the base directory containing next policies for that node (during a generation)
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_ARCHIVE: the full path of the base directory containing previous policies for that node
-
RUDDER_NODE_ROLES: a comma separated list of node’s server role name
node-pre-deletion
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed before a node is deleted.
Typically, these hooks interact with external services using knowledge to validate if the node should actually be deleted.
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_NODE_ID: the nodeId
-
RUDDER_NODE_HOSTNAME: the node fully qualified hostname
-
RUDDER_NODE_POLICY_SERVER_ID: the node policy server id
-
RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE : agent type ("cfengine-nova" or "cfengine-community")
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_CURRENT: the full path of the base directory containing policies for that node
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_NEW: the full path of the base directory containing next policies for that node (during a generation)
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_ARCHIVE: the full path of the base directory containing previous policies for that node
-
RUDDER_NODE_ROLES: a comma separated list of node’s server role name
policy-generation-failed
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_GENERATION_DATETIME : ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time that identifies that policy generation.
-
RUDDER_END_GENERATION_DATETIME : ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time when the generation ended (minus these hooks)
-
RUDDER_ERROR_MESSAGE_PATH : path to a file which contains the full error message of the policy generation failure.
policy-generation-finished
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed after policies are fully generated for all nodes, and these new policies are available for download for the node.
Typically, these hooks are used to log information about the generation which just happened or notify third parties that new policies are available (for ex: cf-serverd SIGHUP)
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_GENERATION_DATETIME : ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time that identifies that policy generation.
-
RUDDER_NODE_IDS_PATH : path to a sourcable file with variable RUDDER_NODE_IDS containing a bash array of node id updated during the process, or the empty array if no nodes were updated.
-
RUDDER_END_GENERATION_DATETIME : ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time when the generation ended (minus these hooks)
-
RUDDER_NUMBER_NODES_UPDATED : integer >= 0; number of nodes updated (could be found by counting $RUDDER_NODE_IDS)
-
RUDDER_ROOT_POLICY_SERVER_UPDATED: 0 if root was updated, anything else if not
policy-generation-node-finished
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed after policies are fully generated for node and made available for the node to download.
Typically, these hooks interact with external services using knowledge from the generated policies (ex: send node-properties JSON file to a third party service).
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_GENERATION_DATETIME : generation datetime: ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time that identify that policy generation start
-
RUDDER_NODE_ID : the nodeId
-
RUDDER_NODE_HOSTNAME : the node fully qualified hostname
-
RUDDER_NODE_POLICY_SERVER_ID : the node policy server id
-
RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE : agent type ("cfengine-nova" or "cfengine-community")
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_CURRENT : new policies directory (for ex for nodes under root: /var/rudder/share/$RUDDER_NODE_ID/rules)
Technically, you could infer RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_NEW, from RUDDER_NODE_ID, but it’s tedious for nodes behind a relay, and it is just simpler not to have to track what are the Rudder internal names, which may change without notice.
policy-generation-node-ready
When/What ?
This directory contains hooks executed after policies are fully generated for node, but before these new policies replace the old ones (technically, before we move /var/rudder/share/$NODEID/rules.new to /var/rudder/share/$NODEID/rules).
Typically, these hooks proceed to sanity checks on the new policies (ex: cf-promises), update permission on files, or interact with external services using information from the generated policies (ex: send node-properties JSON file to a third party service).
Parameters
Hooks parameters are passed by environment variable:
-
RUDDER_GENERATION_DATETIME : generation datetime: ISO-8601 YYYY-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssZ date/time that identify that policy generation start
-
RUDDER_NODE_ID : the nodeId
-
RUDDER_NODE_HOSTNAME : the node fully qualified hostname
-
RUDDER_NODE_POLICY_SERVER_ID : the node policy server id
-
RUDDER_AGENT_TYPE : agent type ("cfengine-nova" or "cfengine-community")
-
RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_NEW: new policies directory (for ex for nodes under root: /var/rudder/share/$RUDDER_NODE_ID/rules.new)
Technically, you could infer RUDDER_POLICIES_DIRECTORY_NEW, from RUDDER_NODE_ID, but it’s tedious for nodes behind a relay, and it is just simpler not to have to track what are the Rudder internal names, which may change without notice.
New directives default naming scheme
When a new directive is created, by default the 'Name' field is filled with the Technique name. For example, if you create a new Directive from the 'Users' Technique, the Name field will get the value: "Users".
This not always what you want, especially for your custom Techniques. So you have the possibility to define new default values for Name, at Technique or at Technique and Version granularity.
This is done by adding or updating the file:
/var/rudder/configuration-repository/techniques/default-directive-names.conf.
That file need to be committed in git, and the Technique library reloaded to take effect:
cd /var/rudder/configuration-repository/techniques/ vi default-directive-names.conf .... git add default-directive-names.conf git commit -m "Change default names for new directives" rudder server reload-techniques
The file format is a simple techniqueId[/optionalVersion]: default name to use format.
The Technique ID is the name of the directory containing the Technique version directory
in /var/rudder/configuration-repository/techniques.
For example, if we imagine that in your company, you have the internal convention to create one directive by user role with the login in the name, you would prefer to have a default value to:
Role <user-role>: <matching-login>
And then, for Users Technique version 7, you changed your mind and now use the scheme:
Role: [user-role] (with login [login])
Then the file will look like:
# Default pattern for new directive from "userManagement" technique: userManagement= Role <user-role>: <matching-login> # For userManagement version 2.0, prefer that pattern in new Directives: userManagement/7.0: Role: [user-role] (with login [login])
Directives ordering
Configuration in Rudder are based on desired states, describing the expected state of the system. However, there are cases where having order is desirable (like ensuring that a JVM is present before deploying an Application server, or ensuring a user is present before setting it sudoers), even if it will converge over the course of several agent runs.
In Rudder, there is two separated ways to order things, depending the type of Technique". So, before that, we need to explain how Policies are generated on the agent from Directives based on the same Technique.
Policy generation and Directive merge
In Rudder, Policies are generated from Directives, but several Directives based on the same Technique always lead to one Policy on the agent. For unique (non multi-instance) Technique, the one with the highest priority is selected. For multi-instance Technique, the different Directive values are merged into one Policy after having been sorted.
|
Separated Policy Generation in Rudder 4.3
In Rudder 4.3, that limitation is lifted and Technique can be made to generate ONE Policy for each Directive. That capacity is controled by the `POLICYGENERATION` tag, where the value `merged` is the pre-4.3 default behavior, and values `separated` or `separated-with-param` lead to one Policy per Directive. See https://issues.rudder.io/issues/10625[Don't merge directive from same technique on generation] for more information. |
Sorting Directives based on the same Technique
For Directive based on the same Technique, the sort order is based on the Priority value of the Directive. Between two Directive, the one with the highest Priority is the first:
-
for a non multi-instance Technique, it means that it is there is only one that is chosen in the resulting Policies (the others are discarded),
-
for a multi-instance Technique, it means that the variables in the Policy will be declared and check in sorting order of Directives (so the first Directive’s variables will be declared in first position and check first during an agent run).
If several Directives have the same Priority, the Rule name, and then the Directive name are used for sorting in alphanumeric order.
|
Priority field value and meaning
The Priority field of a Directive used to be a number, from 0 to 10, where 0 means "highest priority". This changed with https://issues.rudder.io/issues/11725 but if you knew Rudder before that change, please use "0" whenever the documentation says "highest priority". |
Special use case: overriding generic_variable_definition
You can use the merging of Directive to define variable override with the "Generic Variable Definition" Technique.
For example, let say you want to define a DNS variable with default value [default dns] and on some node case, a value [overridden dns]:
-
Create a Directive [1] with high priority: it will be your default case, so set DNS to [default dns].
-
Create an other Directive [2] with lower priority: it will be your specialized case, so set DNS to [overridden dns].
Then, a node with only Directive [1] will have the default value defined, and a node with both Directives will have the overriding one.
It works because on the agent, you can redeclare a variable name and reassign to it a new value: the last one wins (so in our case, the lowest priority).
Sorting Policies
Rudder uses a best-effort method for ordering Policies, based on alphanumeric ordering of the corresponding Rule, then Directive name.
When several Directive were merged, Rudder choose the first (Rule name, Directive name) as the ordering value to use for the resulting Policy.
|
Best practice
You should always start Rules and Directives name by 2 (or 3) digits to be able to easily reorder Policy evaluation if the need happen: Do not use: "My general security rule" and "Check ssh configuration" But use: "05. My general security rule" and "40. Check ssh configuration" |
Example
-
given three Techniques A, B and C
-
directives A1 and A2 based on Technique A, directives B1 and B2 based on B, directives C1 and C2 based on C
-
all Directives have the same priority,
-
rule R0 having [C1], R1 having [A1, B2] and rule R2 having [A2, B1, C2], all applied on a same node,
-
merging (R0, C1) and (R2, C2) ⇒ [C1, C2] and keep (R0, C1) as Policy order
-
merging (R1, A1) and (R2, A2) ⇒ [A1, A2] and keep (R1, A1) as Policy order,
-
merging (R1, B2) and (R2, B1) ⇒ [B2, B1] (because R1 < R2) and keep (R1, B2) for policy order,
-
so policies are sort: (R0, C1) then (R1, A1) then (R1, B2)
-
resulting ordering of directive’s values will be: [C1, C2] then [A1, A2] then [B1, B2]
Share files between nodes
Rudder 4.1 introduced a way to share files from one node to another. It allows a node to send a file to its relay, which will make it available for another target node, that has to to specifically download it.
This file sharing method is secured by:
-
The control of uploaded file signature by the server, to check it matches the source node’s private key.
-
The same mechanism as standard file copy in Rudder to download the shared file from the server.
It also includes a ttl mechanism that allows sharing a file for a limited amount of time.
To use this feature, two generic methods are available in the technique editor:
-
sharedfile_from_node: To download a file shared from another node.
-
sharedfile_to_node: To make a file available to another node.
See the documentation of these methods for details about the required parameters, and especially sharedfile_to_node for a complete usage example.
← Technique editor REST API →